ML009 : GCB (Glucocerebrosidase) Inhibitor
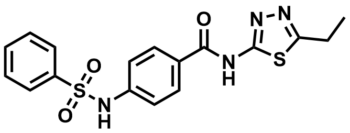
ML009
Target Name
Glucocerebrosidase
Target Alias
GCB
Target Class
Hydrolase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of GCB
Biological / Disease Relevance
Gaucher disease
In Vitro Activity
IC50In Vitro Activity
KiInactive Control
Available
Target Information
Beta-glucocerebrosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-glucocerebroside to glucose and ceramide. The inherited deficiency of beta-glucocerebrosidase results in Gaucher disease, which is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms including hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, bony lesions and bone marrow infiltration with characteristic storage cells, known as Gaucher cells. It is believed that improper folding and trafficking of beta-glucocerebrosidase may contribute to the phenotypes observed. It is suggested that the pharmacological chaperone stabilizes the glucocerebrosidase conformation to prevent misfolding and premature degradation, and helps its trafficking from the ER to its functional site, the lysosome. Therefore, a small molecule beta-glucocerebrosidase inhibitor used as a pharmacological chaperone offers a therapeutic alternative. Not only could it bind to the enzyme to stabilize the conformation and help to improve protein trafficking, but it could also be designed to cross the blood-brain barrier to be used as a potential therapy for neuronopathic Gaucher disease, where currently no efficacious therapy is available.
Properties

ML009
Sulfonamide analogue, 2
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 388.5 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C17H16N4O3S2 | |||
| cLogP | 3.4 | |||
| PSA | 101 | |||
| Storage | -20 | |||
| Solubility | Up to 10mM in DMSO | |||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
CCC1=NN=C(S1)NC(C2=CC=C(NS(=O)(C3=CC=CC=C3)=O)C=C2)=O
InChI:
InChI=1S/C17H16N4O3S2/c1-2-15-19-20-17(25-15)18-16(22)12-8-10-13(11-9-12)21-26(23,24)14-6-4-3-5-7-14/h3-11,21H,2H2,1H3,(H,18,20,22)
InChIKey:
YMGXUJCEBOCIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML009 (CID 2210290, SID 50105141, NCGC 00060210) is observed to be a potent and selective inhibitor of Glucocerebrosidase (GC) Chemotype 2 with an IC50 of 0.074 uM. The selectivity of probe ML009 was measured in 3 other hydrolases including alpha-glucosidase, alpha-galactosidase, and beta-N-acetyldglucosaminidase (HEX). These enzymes are all lipid hydrolases and shared the same metabolic pathways as GC. ML009 is observed to be inactive against these 3 bioassays at concentrations up to 77 uM demonstrating high selectivity to GC. ML009 has been screened against 33 PubChem bioassays and is observed to be active only in the Glucocerebrosidase inhibition assay with an activity value of 0.153 uM.
In vitro assay - Selectivity
| ML009 | iminosugar nonyl-DNJ | |
|---|---|---|
|
glucocerebrosidase |
0.074 uM | 0.103 uM |
|
alpha-glucosidase |
Inactive | 0.050 uM |
|
alpha-galactosidase |
Inactive | Inactive |
|
beta-hexosaminidase |
Inactive | Inactive |
Summary /
Comparative data showing probe specificity for target. The selectivity of ML009 was measured in three other hydrolases including α-glucosidase, α-galactosidase, and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (β-N-acetylhexosaminidase, HEX). Deficiencies in α-glucosidase, α-galactosidase and β-hexosaminidase result in Pompe disease, Fabry disease and Tay-Sachs or Sandhoff disease, respectively, all genetic disorders of lysosomal lipid metabolism similar to Gaucher disease (Vellodi A, 2005). Substrates of these three enzymes labeled with the blue fluorophore 4-methylumbelliferone were used with a GC enzyme assay using the substrate 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (4MU-β−Glc) as control. These four enzyme assays were performed in parallel with the 1536-well plates (Urban DJ, 2008). Results showed that probe ML009 did not inhibit the activities of α-glucosidase, α-galactosidase, or β-hexosaminidase at concentrations up to 77 μM, demonstrating high selectivity to GC. In contrast, the iminosugar nonyl-DNJ was found to inhibit both GC and α-glucosidase, with IC50 values of 0.103 and 0.050 μM, respectively. The IC50 values of the compounds in the GC enzyme assay using the blue fluorogenic substrate 4MU-β−Glc were like those using fluorogenic substrate Res-β-Glc.
Cellular activity - Primary cell (Gaucher fibroblast) assay
| ML009 | N370S | WT (control) |
|---|---|---|
|
4.4 uM |
20% increase in GC activity | 5% increase in GC activity |
|
13.3 uM |
20% increase in GC activity | 0% increase in GC activity |
|
40 uM |
90% increase in GC activity | 20% increase in GC activity |
Summary /
Increase of glucocerebrosidase activity in Gaucher fibroblasts: The primary cells from Gaucher patients with N370S mutations (DMN 87.30) were treated with 4.4, 13.3 and 40 uM of SID 4264637 for 2 days in comparison with the wt. cells (GM5659). A treatment of 40uM inhibitors days resulted in a 40-90% increase of the mutant enzyme (N370S) activity in fibroblasts from Gaucher patients while the increase of normal enzyme activity was much smaller. This result indicates that these inhibitors may stabilize the mutant enzyme protein, help its proper folding/trafficking and thus increase its activity in the cell-based assay.
In vitro assay - Mechanism of Action
Summary /
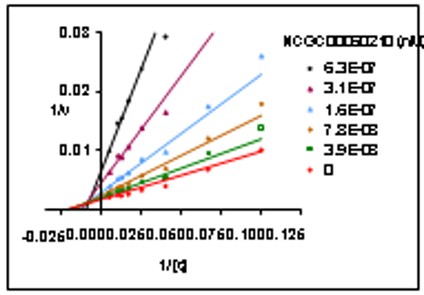
Mechanism of inhibition of probe: The effect of these GC inhibitor SID 4264637 on enzyme kinetics was studied in the enzyme assay to identify the mechanism of inhibition. SID 4264637 exhibited mixed inhibition.
References
- Identification of Modulators of the N370S Mutant Form of Glucocerebrosidase as a Potential Therapy for Gaucher Disease - Chemotype 2.
- Discovery, SAR, and Biological evaluation of Non-Inhibitory Small Molecule Chaperones of Glucocerebrosidase
- Vellodi, A. Lysosomal storage disorders. Br J Haematol 128, 413-431 (2005)
- Urban, DJ et al. Development and Validation of Two Miniaturized Glucocerebrosidase Enzyme Assays for High-Throughput Screening. Combi Chem High Thr Screen. Dec;11(10):817-24. 2008
- Zheng et al. Three classes of glucocerebrosidase inhibitors identified by quantitative high-throughput screening are chaperone leads for Gaucher disease. PNAS 104(32): 13192–13197 (2007)


