ML309 : IDH1 (R132H mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1) Inhibitor
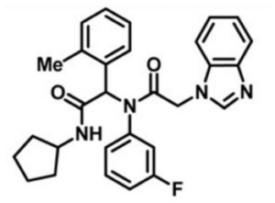
ML309
Target Name
R132H mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1
Target Alias
IDH1
Target Class
Dehydrogenase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of IDH1
Biological / Disease Relevance
R132H mutant IDH1; Glioblastoma; Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML); Isocitrate Metabolism; Cancer Biology; Glioma
In vitro activity
IDH1 R132H IC50In vitro activity
2-HG production in U87MG-IDH1R132H cell IC50In vitro activity
KiTarget Information
The emergence of the role of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) in cancer resulted from genomic sequencing for 22 glioma genomes that found recurrent mutation of IDH1 on chromosome 2q33. Subsequent sequencing of over 900 tumors revealed recurrent IDH mutations in both IDH1 and IDH2 in up to 70% of secondary gliomas and in ~16–17% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases. The mutated residue in IDH1 is most commonly arginine 132, which is most often replaced with either histidine or cysteine. This active site mutation results in loss of activity for metabolism of isocitrate, but confers gain-of function for the production of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG). Herein we describe the quantitative high throughput screening of the R132H mutant IDH1 enzyme and the subsequent medicinal chemistry optimization of the small molecule hit. The resulting ML309 probe (SID 134958858, CID 56832449) is capable of potent and selective inhibition of mutant IDH1 and effectively lowers cell-based production of 2-HG in a U87MG mutant glioblastoma cell line. We hope that this probe leads to important studies into the role of IDH1 as an oncogene, 2HG as an oncometabolite, and can potentially provide opportunities to discover much needed therapies for glioma and AML patients in the future.
Properties

ML309
NCGC00262689
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 484.6 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C29H29FN4O2 | |||
| cLogP | 5.4 | |||
| PSA | 67.2 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 1355446-05-7 | |||
SMILES:
CC1=C(C(C(NC2CCCC2)=O)N(C3=CC=CC(F)=C3)C(CN4C=NC5=CC=CC=C45)=O)C=CC=C1
InChI:
InChI=1S/C29H29FN4O2/c1-20-9-2-5-14-24(20)28(29(36)32-22-11-3-4-12-22)34(23-13-8-10-21(30)17-23)27(35)18-33-19-31-25-15-6-7-16-26(25)33/h2,5-10,13-17,19,22,28H,3-4,11-12,18H2,1H3,(H,32,36)
InChIKey:
GZLNOSRHZLTDMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML309 represents an important compound to study the role of mutant (R132H) IDH1 in cancer cells as well as the metabolic consequences of its expression. As a potent and selective inhibitor of the R132H mutant IDH1 with good cell-based activity, this compound is poised for use in various cellular contexts as well as for potential use in in vivo proof of concept models. The compound has IC s of 96 nM and >35μM against mutant and wild-type IDH1 respectively, and a 500 nM EC in the cell-based 2-hydroxyglutarate production assay. Additionally, ML309 has good in vitro ADME and in vivo PK profile. Though it does not possess significant blood brain barrier (BBB) penetration in healthy mice, use in mice with compromised BBB (as is typically seen in glioblastoma) or the use in AML models is certainly warranted. As a first-in-class molecule with the aforementioned profile, we believe this compound will be quite useful to the scientific community.
In vitro activity - IDH1 R132H Biochemical Assay
| Target | IC50 | Fold Selectivity |
|---|---|---|
|
IDH1 R132H |
96 nM | |
|
IDH1 WT |
36.5 uM | > 380 |
|
U87MG-IDH1R132H cytotoxicity assay |
Inactive |
Summary /
Inhibition of IDH1 R132H was screened by coupling IDH1 R132H-mediated NADPH consumption to a diaphorase/resazurin-based detection assay. Result showed that ML309 increased the fluorescence from resorufin indicating a dose-response inhibition against the R132H mutant (Figure 1).
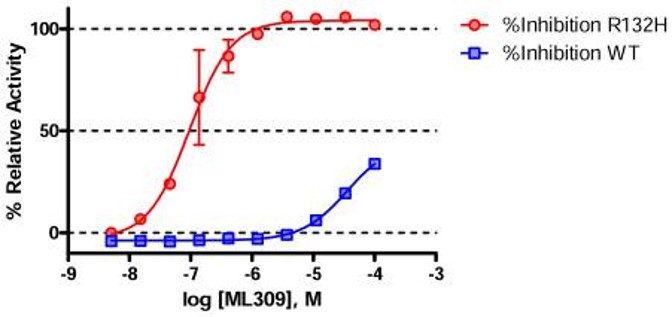
Figure 1. Activity of ML309 against wild type (blue squares) and R132H mutant (red circles) IDH1 determined by the primary diaphorase coupled assay. Each point represents the mean±SD from two duplicate experiments.
In vitro activity - Cellular (2-HG production and Cytotoxicity) Assay
Summary /
ML309 inhibits the IDH1 reaction and decreases the production of 2-HG in IDH1 R132H without cytotoxic effect (Figure 2).
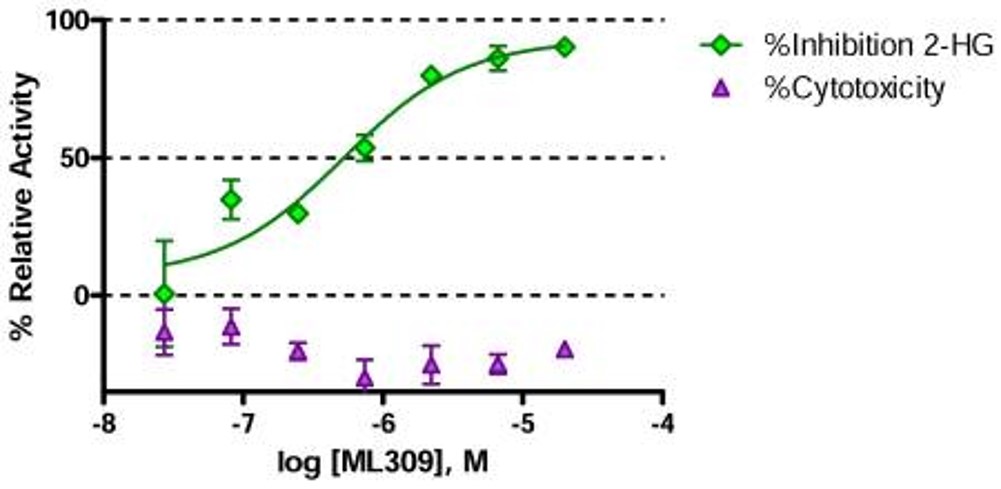
Figure 2. Cell activity of ML309 showing potent reduction of the oncometabolite, 2-HG (green diamonds) in the U87 MG cell based assay with no sign of cytotoxicity (purple triangles). Each point represents the mean±SD from two duplicate experiments.
In vitro activity - Mechanism of Action
Summary /
To determine whether the probe, ML309, was competitive with respect to the substrate α-KG for binding to IDH1 R132H, a mechanism of action study was undertaken (Figure 3). To determine the rate of reaction, the decrease in fluorescence associated with the consumption of the NADPH substrate was monitored directly over time for four concentrations of α-KG and four concentrations of ML309. Result shows the untransformed data, and the large graph shows the Lineweaver-Burk transformation of the data. The lines for the four concentrations of ML309 intersect each other at the y-axis, which indicates that the inhibitor is competitive with respect to the substrate α-KG. Additionally, an estimate of the Ki can be obtained by plotting the inhibitor concentration versus the slopes of the lines in the Lineweaver Burk plot. The Ki obtained from this analysis (156 nM) is similar to the IC50 (96 nM) obtained from the IDH1 R132H diaphorase/resazurin-coupled assay.
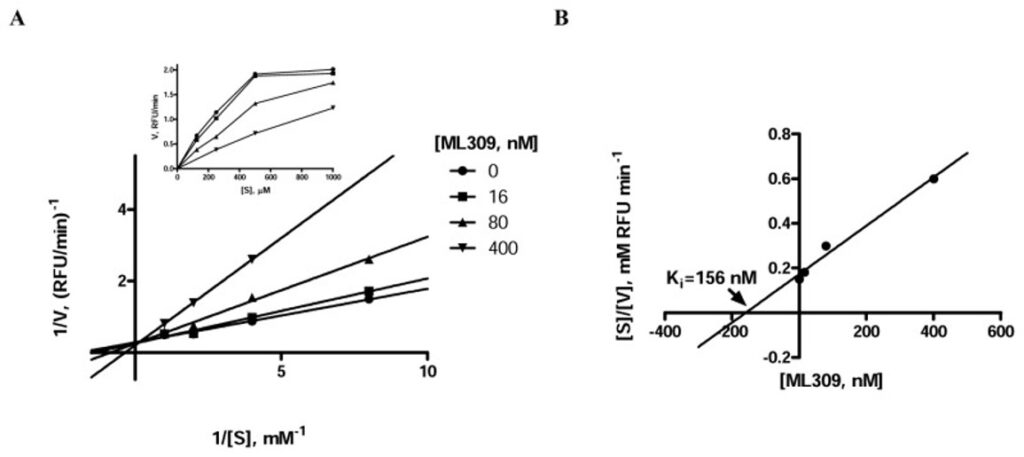
Figure 3. Evaluation of substrate competition of ML309 with α-KG in IDH1 R132H. A) Lineweaver-Burk plot demonstrating competitive mode of inhibition with respect to α-KG; inset shows untransformed data; the data point corresponding to the combination of 400 nM [ML309] and 125 μM [α-KG] did not provide signal above background, hence reaction rate could not be determined. B) Lineweaver Burk plot to determine the Ki for ML309.
In vivo and in vitro activity - ADME Profile and PK Study
| ADME Profile | Aq. Kinetic Solubility (pH 7.4) | Human microsomal Stability, (% remaining at 30 minutes) | Mouse microsomal Stability, (% remaining at 30 minutes) | Human Plasma Stability (% remaining at 30 minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ML309 |
54.3 uM | 6.2 | 7.7 | 97.9 |
Summary /
In vitro assessment of ML309 against mouse and human microsomes, human plasma, aqueous solution and 5 mM glutathione prove that the probe possesses excellent overall stability. Additionally, the >3 hour half life found in the in vivo PK experiment (Figure 4) establish ML309 as molecule stable enough to warrant further in vivo studies.
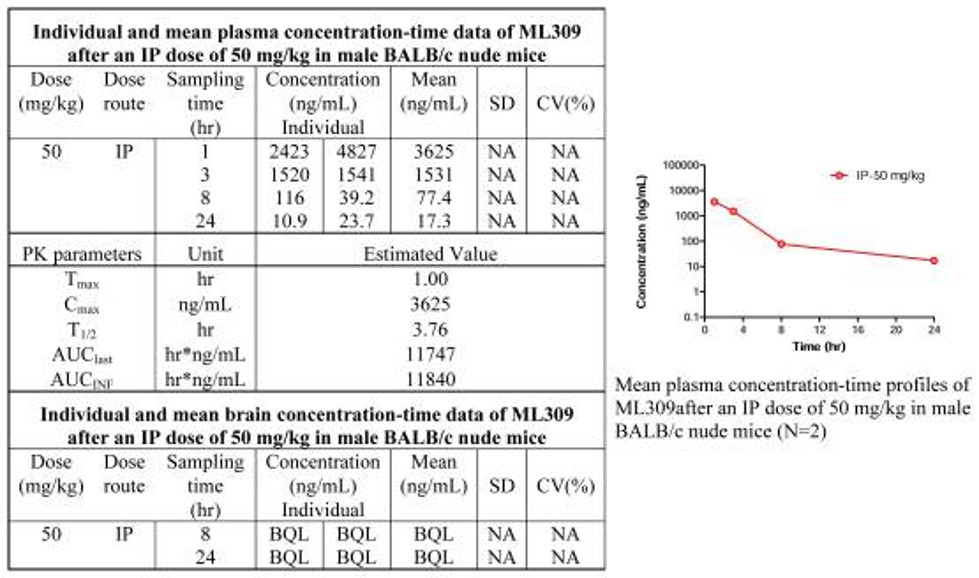
Figure 4. In vivo PK study of ML309
References
- qHTS for Inhibitors of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1): Summary
- Davis M, Pragani R, Popovici-Muller J, et al. ML309: A potent inhibitor of R132H mutant IDH1 capable of reducing 2-hydroxyglutarate production in U87 MG glioblastoma cells. 2012 Apr 16 [Updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-.


