ML384 : NRF2 (Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2) Inhibitor
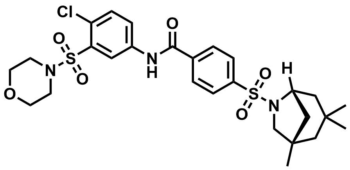
ML384
Target Name
Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2
Target Alias
NRF2
Target Class
Transcription Factor
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of NRF2
Biological / Disease Relevance
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); KEAP1; Cancer Biology
In vitro activity
NRF2 A549 ARE-Fluc assay (IC50)In vitro activity
NRF2 RT-PCR (reduction in gene expression)In vitro activity
GCLM RT-PCR (reduction in gene expression)In vitro activity
NQO1 RT-PCR (reduction in gene expression)In vitro activity
Clonogenic assayIn vivo activity
Tumor xenograph assayTarget Information
Nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor-2 (NRF2), a redox-sensitive transcription factor with frequent gain of function mutations in cancer cells, regulates the expression of energy metabolism related genes, electrophile/ xenobiotic detoxification enzymes, drug efflux proteins and confers chemoresistance and radioresistance and promotes tumor growth. The activity of Kelch like ECH associated protein-1 (KEAP1), an inhibitor of NRF2 signaling, is lost in lung cancer cells by means of somatic loss-of-function mutations, loss of heterozygosity, methylation, etc in a large percentage of non-small cell lung tumors (NSCLC). Increase in NRF2 signaling due to these mutations is associated with decreased recurrence-free and overall survival in patients with NSCLC. Our findings were validated by recent whole genome sequencing of lung tumors by the Cancer Genome Atlas Consortium which identified NRF2-KEAP1 signaling as a key oncogenic pathway dysregulated in lung cancer. These data provide a strong rationale for developing pharmacological inhibitors of NRF2 signaling as a potential cancer therapeutic target. To discover novel NRF2 inhibitors for targeted therapy, we conducted a quantitative high-throughput screen in A549 cells containing a stable NRF2 driven ARE-luciferase construct. These efforts resulted in the identification of three unique chemotypes exemplified by the three probes, ML383NCATS (Patent compound 1, SID 164194503, CID 1298265), ML384NCATS (Patent compound 3, SID 164194504, CID 71741457), and ML385 (Patent compound 4, SID 164194505, CID 1383822).
Properties

ML384
NCGC00343514
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 596.2 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C71H35ClN3O6S2 | |||
| cLogP | 3.8 | |||
| PSA | 130 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
O=C(C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(N2[C@@]3(CC(C)(C[C@](C)(C2)C3)C)[H])=O)NC4=CC=C(C(S(=O)(N5CCOCC5)=O)=C4)Cl
InChI:
InChI=1S/C27H34ClN3O6S2/c1-26(2)15-21-16-27(3,17-26)18-31(21)38(33,34)22-7-4-19(5-8-22)25(32)29-20-6-9-23(28)24(14-20)39(35,36)30-10-12-37-13-11-30/h4-9,14,21H,10-13,15-18H2,1-3H3,(H,29,32)/t21-,27-/m1/s1
InChIKey:
WGQNZRNEUQTGRS-JIPXPUAJSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML384NCATS (Patent compound 3, SID 164194504, CID 71741457) is a probe molecule that inhibits transcription of downstream NRF2 target genes and inhibits colony formation. Furthermore, ML384 demonstrated significant growth inhibition in preclinical xenograft models of lung cancer both as single agents and in combination with carboplatin.
In vitro activity - NRF2 ARE-Luc assay
Summary /
ML384NCATS (patent compound 3) inhibited NRF2 activity in A549 ARE-luciferase assay in a dose response manner (gold circles) but did not affect A549 cell viability (green triangles). Moreover, this probe did not show any broad transcriptional repressor activity as it did not inhibit the HEK293 CMV-Luciferase (blue squares) and the GR-agonist (black squares) counterscreens (Figure 1).
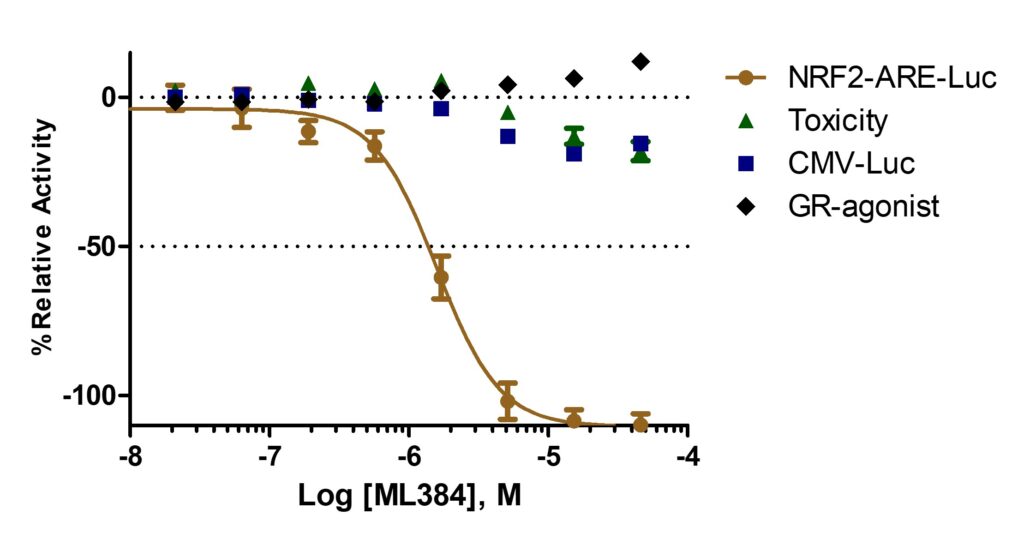
Figure 1. ML384 inhibits NRF2 activity determined through ARE driven Luciferase response (gold circles) in A549 cell line, but does not affect cell viability in that same line (green triangles), and is not a broad transcriptional repressor as judged by activity in a HEK293-CMV-luciferase cell line (blue squares) nor a GR-agonist (black diamonds).
In vitro cellular activity - RT-PCR and Clonogenic assay
Summary /
ML384 (patent compound 3) showed a small reduction of the Nrf2 mRNA expression in the Real time RT-PCR assay after a 10 uM probe treatment for 72 hours. It also reduced the mRNA expression of downstream NRF2 target genes NQO1 but not GCLm. Clonogenic assay showed inhibition of colony formation upon ML383 alone (at 5uM) and in combination with etoposide, carboplatin, and specially with cisplatin (Figure 2).
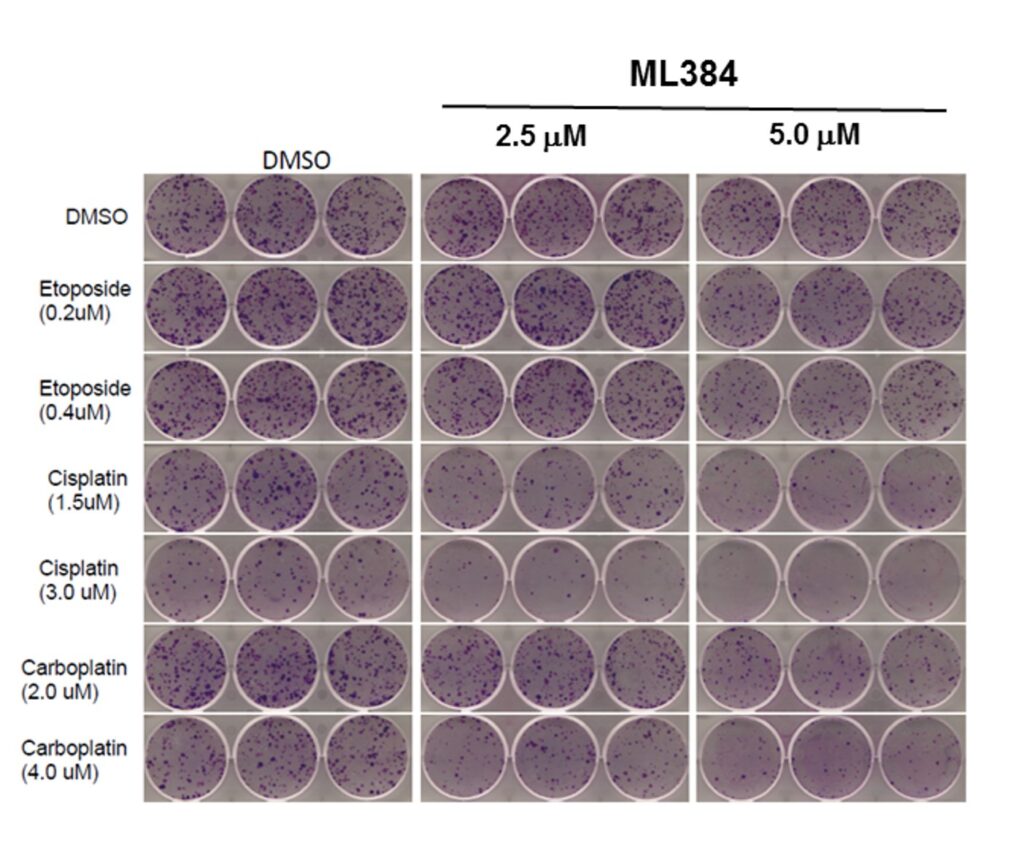
Figure 2. Clonogenic assay in A549 cells for ML384 at 2.5 uM and 5.0 uM, and in combination with etoposide, cisplatin and carboplatin at varying concentrations.
In vivo and vitro activity -ADME and Pharmacokinetic Profiles
| Rat Microsomal Stability (t 1/2) | Mouse Microsomal Stability (t 1/2) | Mouse Plasma Stability (t 1/2) | Aq. Kinetic Solubility (pH 7.4, PBS Buffer) | PAMPA Permeability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ML384 |
4 minutes | 2 minutes | 16 minutes | < 2 uM | < 5 x 10^-6 cm/s |
Summary /
ADME assessment of ML384 (patent compound 3) showed moderate profile with microsomal stability. Kinetic aqueous solubility was poor but due to robust on-target biological activity of the compounds, they were progressed to in vivo PK experiments. ML384 in vivo PK experiments showed a t1/2 = 2.5 hours when dosed IP at 30 mg/kg (Figure 3).
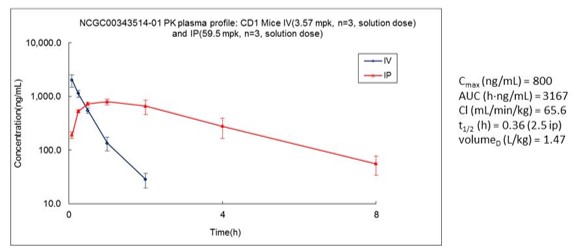
Figure 3. In vivo PK profile of ML384.
In vivo activity - Tumor xenografts
Summary /
ML384 (patent compound 3) showed inhibition in tumor size after 4 weeks of treatment alone. The the decrease in tumor size was more significant with the combination treatment of carboplatin and ML383 (Figure 4). In brief, A549 cells (5 × 106) were injected subcutaneously into the flank of athymic nude mice and tumor dimensions were measured by caliper at an interval of 3-5 days. The tumor volumes were calculated using the following formula: [length (mm) × width (mm) × width (mm) × 0.52]. Once the tumor volumes were approximately 50-100 mm3, mice were randomly allocated into 4 groups: vehicle, small molecule (ML383, ML384, or ML385), carboplatin, small molecule + carboplatin. Vehicle, carboplatin (5 mg/kg daily Monday to Friday), small molecule (30 mg/kg daily Monday to Friday), and a combination of small molecule and carboplatin were administered intraperitoneally for three weeks. At the end of treatment period, mice were sacrificed and tumor, blood, lung, and liver samples were collected. Tumor volume was measured and plotted against sacrificed days (Figure 4).
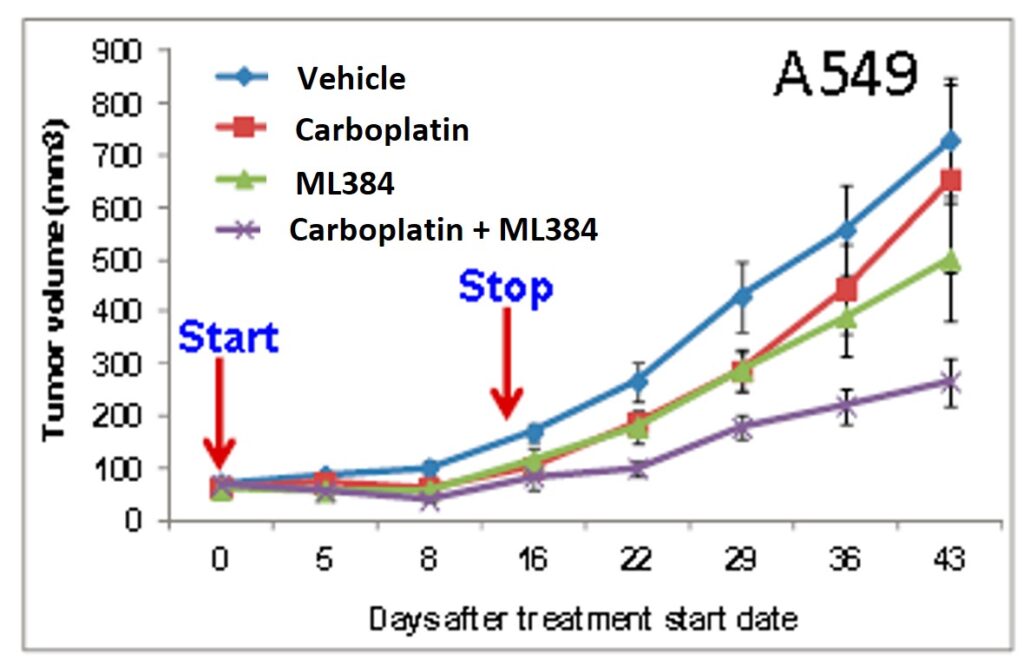
Figure 4. In vivo xenograft experiment with a treatment schedule of vehicle (blue), Carboplatin dosed at 5 mg/kg 5d/wk for 2 wks then stopped (red), ML384 dosed at 60 mg/kg for 5d/wk for 2 wks, then stopped (green), and Carboplatin and ML384 co-dosed at 5 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg respectively, 5d/wk for 2 wks then stopped (purple).


