ML153 : SMN2 (Survival Motor Neuron 2) Modulator
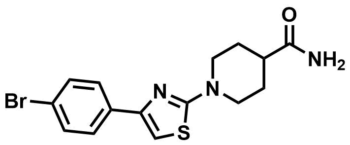
ML153
Target Name
Survival Motor Neuron 2
Target Alias
SMN2
Target Class
RNA Splicing Factor
Mechanism of Action
Modulator of SMN2
Biological / Disease Relevance
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), Splicing Modulator, Gene splicing, SMN2 splicing
In vitro activity
SMN2 reporter (AC50)In vitro activity
ROIIn vitro activity
Luciferase inhibition (IC50)Target Information
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive disorder affecting the expression or function of survival motor neuron protein (SMN) due to the homozygous deletion or rare point mutations in the survival motor neuron gene 1 (SMN1). The human genome includes a second nearly identical gene called SMN2 that is retained in SMA. SMN2 transcripts undergo alternative splicing with reduced levels of SMN. Up-regulation of SMN2 expression, modification of its splicing, or inhibition of proteolysis of the truncated protein derived from SMN2 have been discussed as potential therapeutic strategies for SMA. In this manuscript, we detail the discovery of a series of arylpiperidines as novel modulators of SMN protein. Systematic hit-to-lead efforts significantly improved potency and efficacy of the series in the primary and orthogonal assays. Structure property relationships including microsomal stability, cell permeability and in vivo pharmacokinetics (PK) studies were also investigated. We anticipate that a lead candidate chosen from this series may serve as a useful probe for exploring the therapeutic benefits of SMN protein up-regulation in SMA animal models, and a starting point for clinical development.
Properties

ML153
MLS000698854
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 366.28 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C15H16BrN3OS | |||
| cLogP | 3.1 | |||
| PSA | 87.5 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 361371-42-8 | |||
SMILES:
O=C(N)C1CCN(C2=NC(=CS2)C=3C=CC(Br)=CC3)CC1
InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H16BrN3OS/c16-12-3-1-10(2-4-12)13-9-21-15(18-13)19-7-5-11(6-8-19)14(17)20/h1-4,9,11H,5-8H2,(H2,17,20)
InChIKey:
YWCKNSAYJDPHQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
Two lead series represented by the 5-methoxy-3,6-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazine (compound 1) and 1-(4-(4-bromophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide (compound 2, ML153 (SID 87677807, CID 990823, NCGC00183533), were able to increase the luciferase signal in the SMN2 reported assay and increase SMN protein production in a dose dependent manner in the western blot. Although the specific mechanism of action is unknown, ML153 increased the expression of SMN2 but reduced the expression of SMN1. This reduction of SMN1 expression would not be relevant in vivo, due to the fact that the SMN1 gene is not functional at all in SMA patients. ML153 also possessed a more tractable SAR and drug-like properties; and displayed high cell permeability in Caco-2 cell permeability assay with no indication of being a glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate.
In vitro activity - SMN2 Luciferase Reporter Assay and SMN Western Blot
Summary /
ML153 (Figure 1A compound 2) increase the SMN2 reporter assay signal indicating a potential up-regulation of SMN2 expression or modification of its splicing (Figure 1B). This is further validated by the increase in the western blot of SMN levels after treatment with compounds (Figure 1C).
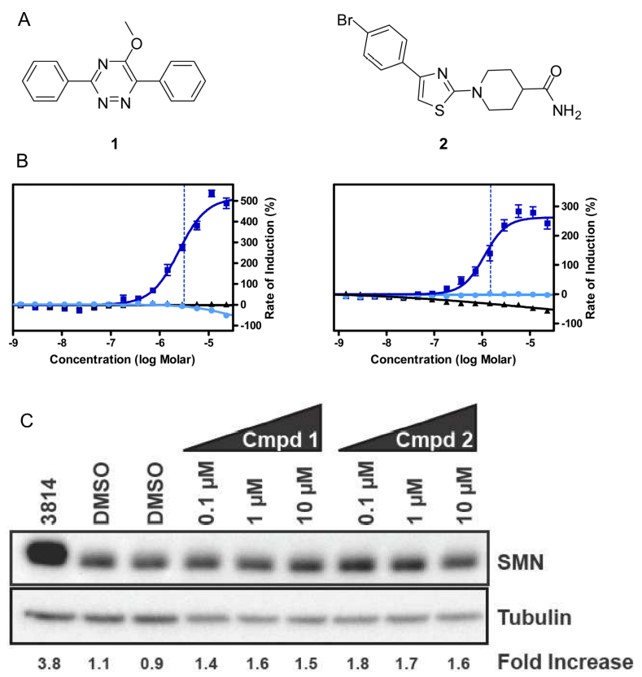
Figure 1. A) Chemical structures of 1 and 2 from qHTS. B) Activity of compounds 1 and 2 (ML153) in SMN1 (cyan) and SMN2 (blue) reporter assays, indicating the rate of SMN induction (ROI) at different concentrations, and luciferase inhibition assay (black). C) Quantification by western blot of SMN levels after treatment with compounds 1 and 2 at different concentrations, as indicated.
In vitro activity - ADME properties
| Compound | Mouse liver microsome T1/2 (min) | Caco-2 Permeability mean Papp A → B (10^−6 cm/s) | Caco-2 Permeability mean Papp B → A (10^−6 cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ML153 |
12 | 30.7 | 12.1 |
Summary /
Microsomal stability analysis was performed by Cerep and are based upon duplicate incubations of test reagent with mouse liver microsomes at 37 °C as described (www.cerep.com). LC/MS/MS is utilized to quantitate remaining test compound. Test compounds were applied at standard concentrations (1 µM). Caco-2 permeability analysis was performed by Cerep as described (www.cerep.com). Data are expressed in Papp (apparent permeability) in 10−6 cm s−1. Colchicine and Ranitidine were used as a low permeability controls (Colchicine: mean A→B < 0.1 and mean B→A = 7.9; Ranitidine mean A→B = 0.2 and mean B→A = 2.8), Propranolol was used as a high permeability control (mean A→B = 41.0 and mean B→A = 39.4) and Labetalol was used as a P-gp substrate control (mean A→B = 7.3 and mean B→A = 36.6). Test compounds were applied at standard concentrations (10 µM).
References
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen for Enhancers of SMN2 Splice Variant Expression: Summary
- Xiao J, Marugan JJ, Zheng W, Titus S, Southall N, Cherry JJ, Evans M, Androphy EJ, Austin CP. Discovery, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel SMN protein modulators. J Med Chem. 2011 Sep 22;54(18):6215-33. doi: 10.1021/jm200497t. Epub 2011 Aug 19. PMID: 21819082; PMCID: PMC3174349.
- Marugan, Juan Jose; Xiao, Jingbo; Titus, Steven A.; Southall, Noel; Zheng, Wei; Androphy, Elliot J.; Cherry, Jonathan World Intellectual Property Organization, WO/2011/130515
- Murugan, JJ. et al. US20130096160 - ARYLTHIAZOLYL PIPERIDINES AND RELATED COMPOUNDS AS MODULATORS OF SURVIVAL MOTOR NEURON (SMN) PROTEIN PRODUCTION.


