ML063 : NFkB (Nuclear factor kappa B) Inhibitor

ML063
Target Name
Nuclear factor kappa B
Target Alias
NFkB
Target Class
Transcription Factor
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of NFkB
Biological / Disease Relevance
NFκB complex pathway; IκB kinase (IKK); IκBα stabilization; Cancer Biology; NFκB p65 translocation
In vitro activity
NFκB Translocation Assay (IC50)In vitro activity
NFκB β-lactamase Assay (IC50)In vitro activity
IκBα Stabilization Assay (EC50)Target Information
Nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) is the designation for a collection of transcription factors including homo- and heterodimers of the Rel family proteins (p50, p52, c-Rel, RelA/p65 and RelB). First described in 1986 as an enhancer of immunoglobulin-κ, NFκB is now understood to bind to the promoter region of more than 400 genes and play an important role in numerous physiological events, most prominently as a primary regulator of the immune and inflammatory responses. Several pathways leading to activation of NFκB are currently understood. Within the canonical pathway, the NFκB heterodimer exists predominantly in the cytoplasm as an inactive complex with the inhibitory IκB proteins. Phosphorylation of the IκB proteins by an IκB kinase (IKK) targets the IκBα protein for polyubiquitination by an E3 ligase and degradation by the proteasome. This permits the NFκB complex to translocate to the nucleus and commence gene expression. The exploration of this pathway has given the biomedical community several potential targets for manipulation of NFκB activity including IKK inhibition, proteasome regulation, and transcriptional inhibitors of NFκB. Therefore, NFκB has emerged as a highly studied therapeutic target and small molecule regulation of signaling cascades associated with NFκB may provide novel approaches to alleviate numerous disease states.
Properties

ML063
MLS000038106
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 282.3 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C15H10N2O2S | |||
| cLogP | 2.4 | |||
| PSA | 67.4 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | 10mM stock in DMSO | |||
| CAS Number | 21868-80-4 | |||
SMILES:
O=S1(=O)NC2=C(C=CC3=CC=CN=C23)C4=CC=CC=C14
InChI:
InChI=1S/C15H10N2O2S/c18-20(19)13-6-2-1-5-11(13)12-8-7-10-4-3-9-16-14(10)15(12)17-20/h1-9,17H
InChIKey:
CYSOFAOLQAYKGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML063 (NCGC00070544, SID 26752300, CID 659101) is a member of the N-(quinolin-8-yl)benzenesulfonamides series capable of suppressing the NFkappaB pathway identified from two high-throughput screens run at two centers of the NIH Molecular Libraries Initiative. These small molecules were confirmed in both primary and secondary assays of NFkappaB activation and expanded upon through analogue synthesis resulting to the probe compound ML063.
In vitro activity - Probe SAR and Selectivity Assay
| IκBα Stabilization (EC50) | Cytotoxicity Assay (IC50) | |
|---|---|---|
|
ML063 |
2.2 uM | Inactive |
Summary /
To further confirm that ML063 (Xie Y et al, compound 5) interfered with the NFκB activation in a genuine manner, a reporter assay obtained from Invitrogen where induction of β-lactamase occurred in an NFκB-dependent manner was also performed on the probe and its analogs. This data confirmed the ability of these compounds to inhibit the NFκB pathway with minimal or no cytotoxic effect. A full screen for proteasome inhibition (PubChem AID: 526) against the library that included the leads described here did not yield any actives other than MG-132. As well, selected compounds were screened versus a panel of
kinases including IKKα, IRAK1, IRAK4, JNK1α1, JNK2α2, JNK3, MAPK1, MAPK2, PKBα, RIPK2, SAPK2a, TAK1, and TBK1 without any inhibition. An E3 ligase target was ruled out by treating HUVEC with ML063 and staining for phosphorylated IκBα. Treatment of HUVEC with Ro106-9920, a known E3 ligase inhibitor, but not ML063, blocked IκBα ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation, resulting in detectable staining of IκBα. Thus, the target of this class of small molecule NFκB pathway inhibitors has not been identified at present.
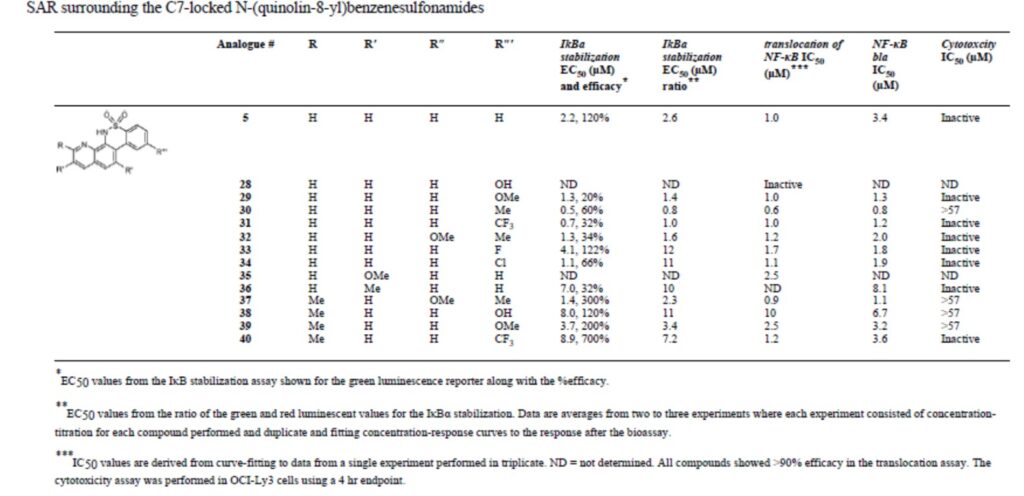
Table 1: Structure-activity relationships (SAR) surrounding the C7-locked N-(quinolin-8-yl)benzenesulfonamides.
References
- Xie Y, Deng S, Thomas CJ, Liu Y, Zhang YQ, Rinderspacher A, Huang W, Gong G, Wyler M, Cayanis E, Aulner N, Többen U, Chung C, Pampou S, Southall N, Vidović D, Schürer S, Branden L, Davis RE, Staudt LM, Inglese J, Austin CP, Landry DW, Smith DH, Auld DS. Identification of N-(quinolin-8-yl)benzenesulfonamides as agents capable of down-regulating NFkappaB activity within two separate high-throughput screens of NFkappaB activation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jan 1;18(1):329-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.10.100. Epub 2007 Oct 30. PMID: 18024113; PMCID: PMC2275118
- IkB Signaling qHTS
- Primary HTS assay for chemical potentiators of IL-1B stimulated NFkB nuclear translocation
- Davis RE, Zhang YQ, Southall N, Staudt LM, Austin CP, Inglese J, Auld DS. A cell-based assay for IkappaBalpha stabilization using a two-color dual luciferase-based sensor. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2007 Feb;5(1):85-103. doi: 10.1089/adt.2006.048. PMID: 17355202
- PubChem AID 526: Ubiquitin-GFP Assay


