ML091 : Cruzain (T. cruzi Cruzipain) Inhibitor
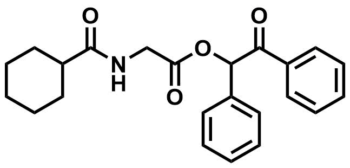
ML091
Target Name
T. cruzi Cruzipain
Target Alias
Cruzain
Target Class
Cysteine Endopeptidase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of Cruzain
Biological / Disease Relevance
Anti-trypanosomal agent, Chagas disease
In vitro activity
Cruzain qHTS (EC50)In vitro activity
Rhodesain (EC50)In vitro activity
TbCatB (EC50)In vitro activity
Cruzain Cuvette Assay (EC50)Target Information
Cruzain is a key cysteine protease in Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi); it is essential for the parasite survival and replication, and has been validated as a drug target for this organism. Trypanosoma cruzi, a protozoan parasite, is the causative agent of Chagas disease. This is a major neglected tropical disease affecting over 16 million people, primarily in Central and South America. Discovering novel inhibitors of cruzain and determining their enzyme-bound structures is expected to provide a platform for drug discovery efforts against this resistance target.
Project Team
Properties

ML091
NCGC00181213
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 379.45 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C23H25NO4 | |||
| cLogP | 4.6 | |||
| PSA | 72.47 A^2 | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 1222659-69-9 | |||
SMILES:
C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)NCC(=O)OC(C2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3
InChI:
InChI=1S/C23H25NO4/c25-20(16-24-23(27)19-14-8-3-9-15-19)28-22(18-12-6-2-7-13-18)21(26)17-10-4-1-5-11-17/h1-2,4-7,10-13,19,22H,3,8-9,14-16H2,(H,24,27)
InChIKey:
XUWBMGZNJBLYOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML091 (CID 44143092; SID 99206570) exhibits potent near-stoichiometric inhibition of Cruzain and should be useful as both a potent effector of the enzyme in vitro and as a starting point for development of anti-trypanosomal agents. ML091 belongs to a compound series that has been shown to be a non-covalent reversible inhibitor of Cruzain. ML091 probe displays potent reversible covalent inhibition of both cruzain and rhodesian which are two homologous cysteine proteases. ML091, was found to have minimal effect on the T. Cruzi parasite and have not shown potency against the parasites (in vivo). As such, this probe is best suited for in vitro studies of Cruzain, where a potent and selective non-covalent inhibitor is preferred.
In vitro activity - Biological assays
Summary /
ML091 displays potent reversible non-covalent inhibition of two homologous cysteine proteases cruzain and rhodesian. Moreover, this probe showed less to none cytotoxic activity towards T. brucei cell culture assay (Figure 1).
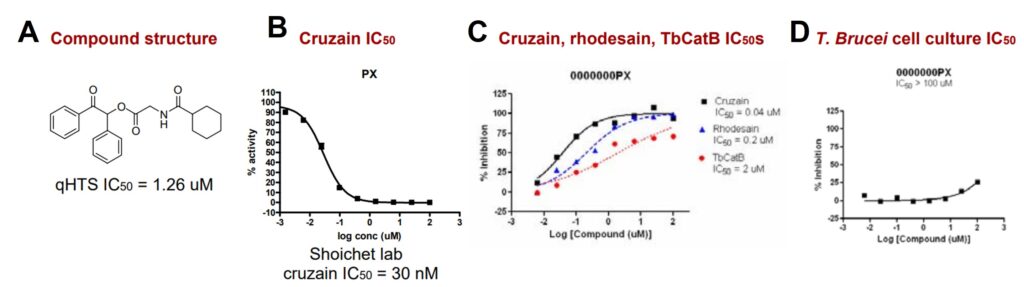
Figure 1. Biological activity of ML091. A) Chemical structure of the probe. B) Secondary cruzain cuvette assay performed at Shoichet lab. C) Dose response assay of ML091 against cruzain, rhodesain, and TbCatB. D) Cytotoxicity assay against ML091.
In vitro activity - Selectivity Assay
| Cruzain qHTS (EC50) | Papain (EC50) | Selectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ML091 |
1260 nM | >50000 nM | 40:1 |
Summary /
Papain (counterscreen assay), another cysteine protease (related to cruzain) known to utilize the same Z-FR-AMC fluorogenic substrate, was selected as a convenient profiling target to determine selectivity of the probe. ML091 is found to be more selective against Cruzain than against Papain.
References
- Probe Development Summary of Inhibitors of Cruzain
- Probe Development Summary of Promiscuous Inhibitors (Artifacts) of Cruzain
- Mott BT, Ferreira RS, Simeonov A, Jadhav A, Ang KK, Leister W, Shen M, Silveira JT, Doyle PS, Arkin MR, McKerrow JH, Inglese J, Austin CP, Thomas CJ, Shoichet BK, Maloney DJ. Identification and optimization of inhibitors of Trypanosomal cysteine proteases: cruzain, rhodesain, and TbCatB. J Med Chem. 2010 Jan 14;53(1):52-60. doi: 10.1021/jm901069a. PMID: 19908842; PMCID: PMC2804034
- Luci D, Lea W, Ferreira R, et al. Reversible and non-covalent benzimidazole-based in vivo lead for Chagas disease. 2011 Apr 15 [Updated 2013 Feb 28]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK133417/


