ML062 : Pol III HE (DNA Polymerase III Holoenzyme, Polymerase Core Enzyme) Inhibitor
ML062
Target Name
DNA Polymerase III Holoenzyme, Polymerase Core Enzyme
Target Alias
Pol III HE
Target Class
Polymerase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of Pol III HE
Biological / Disease Relevance
Antibacterial; DNA replication machinery of infectious organisms; Pol III HE; E. coli DNA polymerase
In vitro activity
Holoenzyme qHTS (IC50)In vitro activity
Polymerase Core Assay (IC50)In vitro activity
Core / Holoenzyme RatioTarget Information
The process of DNA replication is central to the propagation of all bacteria. To date, no commercially available antibacterial targets any of the enzymes that make up the central replication system in bacteria. The DNA replication machinery of infectious organisms therefore stands as an unexplored target for drug development efforts and presents a significant opportunity. Replication has not previously been targeted in large part because its complexity poses a formidable technological barrier to setting up HTS assays. In addition, since activity of many individual subunits depends on proper association with other components of the replication apparatus, target-based assays using single subunits are generally not feasible. A substantial portion of the system must therefore be reconstituted for drug screening. In this proposal, we present a plan to develop and adapt assays where protein components of the bacterial replication apparatus work together in complex DNA replication reactions. The DNA Polymerase III Holoenzyme (Pol III HE) of bacteria contains approximately 10 subunits that undergo marked changes in protein-protein association during each of nearly 20 identified kinetic steps of the complex processive reaction they catalyze. Since all of these proteins must function together, the ca. 100 distinct interactions and catalytic events all provide targets for antibacterial action, and thus provide a multiple of the proteins present as targets. We have developed a simple fluorescence-based assay, and have adapted this format to a high throughput screen. Such assays are expected to be profoundly more efficient compared to traditional screening assays using single target enzymes, since activities of each of the proteins that comprise the holoenzyme are targeted simultaneously. We anticipate this will increase the number and the quality of hits obtained from screening the MLSCN collection, thereby providing a richer variety of inhibitors for further development and, in turn, appreciably increasing the odds of successfully identifying effective and novel antibacterials.
Early work in McHenry’s laboratory established the feasibility of assaying for double stranded DNA production of a reconstituted E. coli DNApol III holoenzyme system, consisting of DNA Polymerase III – (αεθ)2τ3δδ’χψ, β subunit – processivity factor, SSB – single-stranded DNA binding protein, and Primase. Inhibition of polymerase activity was screened by measuring the production of double-stranded DNA via PicoGreen fluorescence increase. A fully-automated qHTS experiment was performed against a collection of 71,028 compounds tested as 7- to 15-point concentration series at 4 uL reaction volume in 1536-well plate format. Actives identified from the screen were subjected to confirmatory experiments using the screening assay and subsequently against the individual targets in deconvolution assays.
Properties

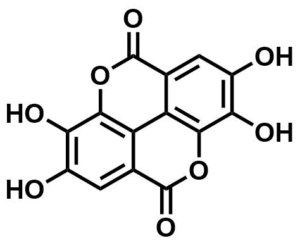
ML062
Ellagic Acid
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 302.19 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C14H6O8 | |||
| cLogP | 1.1 | |||
| PSA | 134 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | 10 mM stock in DMSO | |||
| CAS Number | 476-66-4 | |||
SMILES:
C1=C2C3=C(C(=C1O)O)OC(=O)C4=CC(=C(C(=C43)OC2=O)O)O
InChI:
InChI=1S/C14H6O8/c15-5-1-3-7-8-4(14(20)22-11(7)9(5)17)2-6(16)10(18)12(8)21-13(3)19/h1-2,15-18H
InChIKey:
AFSDNFLWKVMVRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML062 (NCGC00017245, SID 11113162, CID 5281855) is observed to inhibit the E. coli DNA Polymerase III with higher selectivity towards the holoenzyme.
In vitro activity - Target Deconvolution Assays
| Holoenzyme (IC50) | Clamp Loader (IC50) | Clamp Loader/ Holoenzyme Ratio | Primase (IC50) | Primase/ Holoenzyme Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ML062 |
2.27 nM | 180 nM | 79 | 180 nM | 79 |
Summary /
ML062 inhibits DNA polymerase III holoenzyme with potency in the nanomolar range. This probe is also observed to inhibit the polymerase core enzyme and primase. To evaluate the probes activity, a target deconvolution assays were performed. It is broken down into 3 different reaction stages (Priming, Initiation complex formation and Elongation). Assays for each stage have been developed and used to determine the mechanism of action of inhibitors of the Holoenzyme (Figure 1). Primase Assay measures the synthesis of an RNA primer by dnaG Primase on SSB-coated M13Gori Phage DNA. Clamp-Loader ATPase Assay measures the hydrolysis of ATP concomitant with the loading of a b processivity clamp on a model primer-template. Gap Filling DNA polymerase Assay measures the distributive DNA synthesis of DNA Polymerase III Core (aeq) on DNase I activated Calf Thymus DNA.
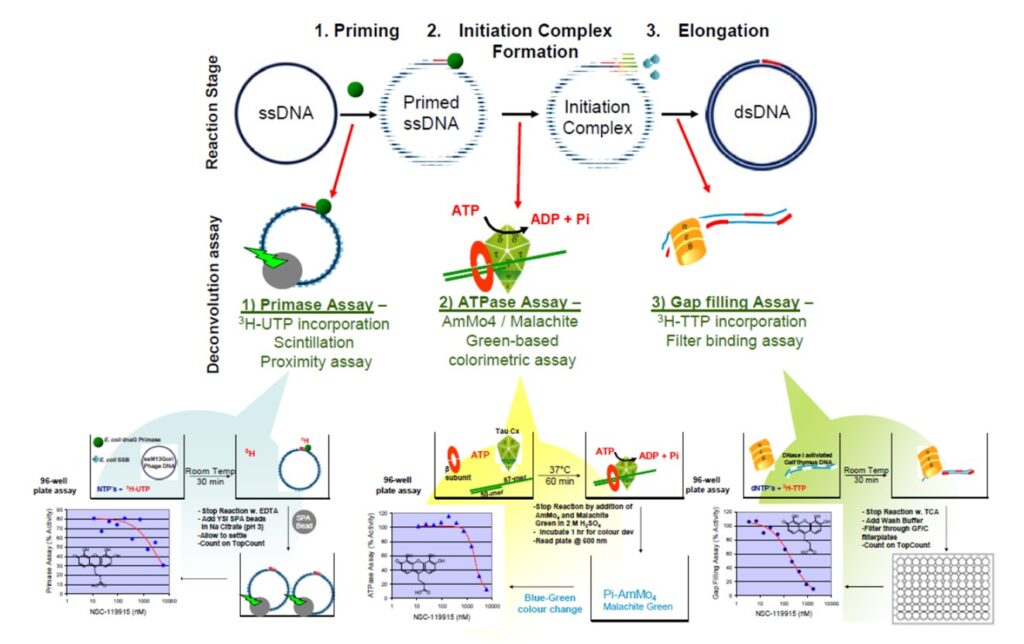
Figure 1. Target deconvolution Assays. Shown is the multistep process leading to a synthesis of a new DNA strand starting from a single-stranded template and NTPs/dNTPs via the catalytic action of the holoenzyme complex. Below, the three distinct steps of the process: creation of short RNA primer (primase), the initiation of DNMA Synthesis (clamp loader), and the processive strand extension (polymerase core) are indicated, along with the respective assays used to address the specific reaction components.
References
- qHTS Assay for Inhibitors of DNA Polymerase III Holoenzyme System
- Marians KJ, Hiasa H, Kim DR, McHenry CS. Role of the core DNA polymerase III subunits at the replication fork. Alpha is the only subunit required for processive replication. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 23;273(4):2452-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.4.2452. PMID: 9442096.
- Kim DR, Pritchard AE, McHenry CS. Localization of the active site of the alpha subunit of the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1997 Nov;179(21):6721-8. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.21.6721-6728.1997. PMID: 9352922; PMCID: PMC179601.
- Seville M, West AB, Cull MG, McHenry CS. Fluorometric assay for DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptase. Biotechniques. 1996 Oct;21(4):664, 666, 668, 670, 672. doi: 10.2144/96214st04. PMID: 8891218.


