ML109 : TSHR (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor) Agonist
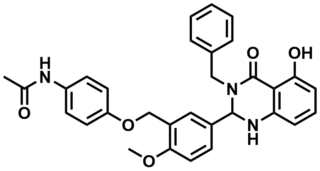
ML109
Target Name
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor
Target Alias
TSHR
Target Class
G-protein Coupled Receptor
Mechanism of Action
Agonist of TSHR
Biological / Disease Relevance
Thyroid homeostasis, TSHR biology
In vitro activity
TSHR qHTS (EC50)In vitro activity
TSHR cAMP ELISA (EC50)Target Information
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is a heterodimeric glycoprotein hormone that regulates thyroid homeostasis upon interaction with the TSH receptor (TSHR). TSH binds to the TSH receptor, which couples preferentially to the G-alpha (s) (Gs) protein, resulting in activation of adenylate cyclase and increase in cyclic adenosine 3’, 5’ monophosphate (cAMP). In this report, we describe the discovery and SAR studies of a series of dihydroquinazolin-4-ones as TSHR agonists. ML109 (CID 25246343) is the first selective and orally available small molecule TSHR agonist, and the probe will be a useful pharmacological tool to study TSHR biology in thyroidal and extra thyroidal tissues.
Properties

ML109
MLS002576689
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 523.6 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C31H29N3O5 | |||
| cLogP | 5.1 | |||
| PSA | 100 | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | 10 mM in DMSO | |||
| CAS Number | 1186649-91-1 | |||
SMILES:
CC(NC1=CC=C(OCC2=C(OC)C=CC(C3NC4=C(C(N3CC5=CC=CC=C5)=O)C(O)=CC=C4)=C2)C=C1)=O
InChI:
InChI=1S/C31H29N3O5/c1-20(35)32-24-12-14-25(15-13-24)39-19-23-17-22(11-16-28(23)38-2)30-33-26-9-6-10-27(36)29(26)31(37)34(30)18-21-7-4-3-5-8-21/h3-17,30,33,36H,18-19H2,1-2H3,(H,32,35)
InChIKey:
JRVXFGNCHKHBPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML109 (SID 26755506; CID 25246343) is a member of a series of TSHR agonists. The current state of the art is lacking any small molecule TSHR agonists. This probe can be used to study TSHR functions in vitro and in vivo, and could be used as a lead for development of drugs to replace recombinant human TSH in patients with thyroid cancer. It is highly selective for human TSHR over other glycoprotein hormone receptors, such as LHCGR and FSHR, and interacts with the receptor’s serpentine domain. In primary cultures of human thyrocytes, this compound increases mRNA levels for thyroglobulin, thyroperoxidase, sodium iodide symporter, and deiodinase type 2, as well as deiodinase type2 enzyme activity. Moreover, oral administration of the agonist stimulated thyroid function in mice, resulting in increased serum thyroxine and thyroidal radioiodide uptake.
In vitro activity - Selectivity Assay
| ML109 (EC50) | |
|---|---|
|
TSHR |
7.9 uM |
|
FSHR |
> 100 uM |
|
LHR |
> 100 uM |
Summary /
ML109 is observed to be > 10 fold selective against TSHR vs FSHR or LHR. TSH, Luteinizing Hormone (LH), and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) all belongs to the glycoprotein hormone family (Vassart 2004).
In vitro activity - ADME Profiling Assay
| Study | Result | Result 2 |
|---|---|---|
|
Turbidometric aqueous solubility |
EPR = 2.0 uM | |
|
Microsomal stability |
Clint = 195 | t 1/2 = 7.1 min |
|
Bi-directional Caco-2 permeability |
Papp = 38.6 (A-B) | Papp = 11.8 (B-A) |
|
Pgp substrate identification |
Efflux Ratio = 0.25 | |
|
5-isoform / substrate CYP inhibition |
> 25 uM | |
|
Plasma protein binding |
fu = 0.14 |
Summary /
In vitro ADME studies were performed on the probe ML109. This data indicates that the probe precipitates out of solution at 2 μM, and exhibits a high rate of clearance and good absorption. Additionally, the probe does not inhibit CYP, and is modestly affected by the Pgp inhibitor.
In vivo activity - Thyroxine (T4) secretion and thyroidal radioiodide uptake in mice.
Summary /
In vivo studies showed that CID 25246343/ML109 could increase secretion of T4 and thyroidal iodide uptake in mice after administration by esophageal gavage, suggesting this probe is an orally available small molecule that can stimulate thyroid gland function (Neumann 2009).
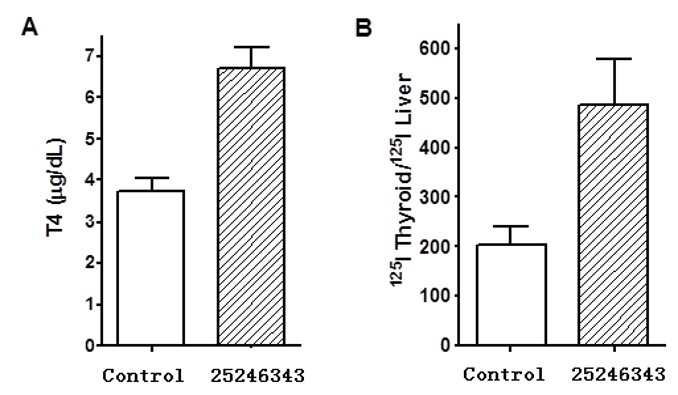
Figure 1. Stimulation by CID 25246343/ML109 of thyroxine (T4) secretion and thyroidal radioiodide uptake in mice. A: Vehicle (PEG 300, control) or CID 25246343/ML109 (2.5 mg) was given by esophageal gavage and serum T4 was measured 2 hr later. B: Vehicle (control) or CID 25246343/ML109 (2.5 mg) was given by esophageal gavage on days 1 and 2. On the morning of the 3rd day, Na125I (20 μCi) was administered by esophageal gavage and the mice were sacrificed 2 hr later. The thyroid glands and small pieces of liver were excised and counted for 125I radioactivity. The data are presented as the ratio of radioactivity in the thyroid/liver.
In vitro activity - Mechanism of Action
Summary /
There have been several studies to validate the probe’s exact binding site on TSHR. It was predicted to bind to the serpentine domain of TSHR, which is different from the amino terminal ectodomain binding site of endogenous TSH. This was validated by testing its binding to a TSHR mutant with the aminoterminal ectodomain deleted (KFLR). KFLR is not activated by TSH, but the probe molecule did activate KFLR, albeit with 12% lower efficacy and lower potency (EC50 = 1.7 μM). The binding was then modeled and N5.47 was predicted to be critical for activity, and a site specific mutant validated this prediction (Neumann 2009).
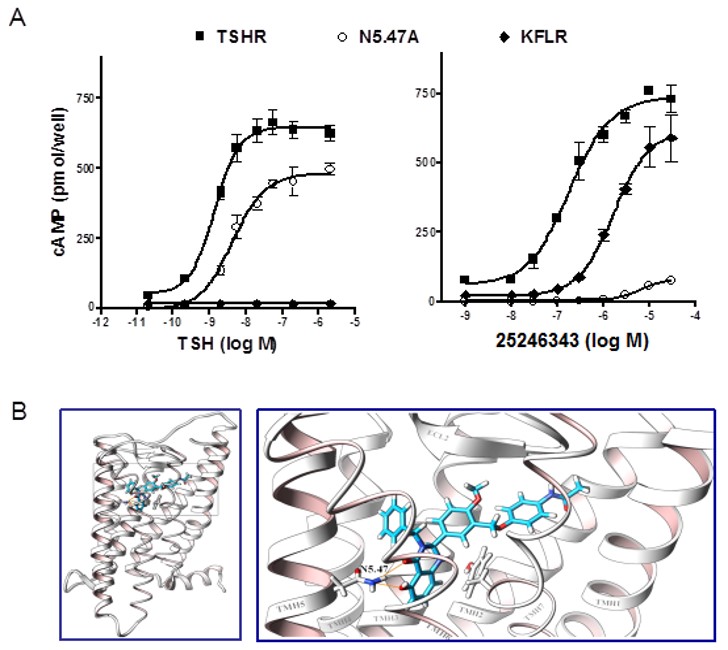
Figure 2. CID 25246343/ML109 activates TSHR by binding to the transmembrane helical bundle. A The effects of CID 25246343/ML109 or TSH on cAMP accumulation in cells expressing TSHR, TSHR-KFLR in which the large amino-terminal ectodomain to which TSH binds, is deleted, or N5.47A in which Asn at position-5.47 was mutated to Ala. B Docking of CID 25246343/ML109 into the homology model of TSHR predicts CID 25246343/ML109 binds within the transmembrane helical bundlen (left panel). Enlargement of the boxed region in the left panel (right panel) shows an interaction of CID 25246343/ML109 with an Asn in TMH5 (N5.47).
References
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen for Agonists of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor: Summary
- Titus S, Neumann S, Zheng W, et al. Quantitative high-throughput screening using a live-cell cAMP assay identifies small-molecule agonists of the TSH receptor. J Biomol Screen. 2008;13(2):120-127
- Titus S, Huang W, Marugan J, et al. Identification of Potent and Selective Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor Agonists. 2009 Sep 1 [Updated 2011 Mar 25]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010
- Neumann S, Huang W, Titus S, et al. Small-molecule agonists for the thyrotropin receptor stimulate thyroid function in human thyrocytes and mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(30):12471-12476. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904506106
- Neumann S, Padia U, Cullen MJ, et al. An Enantiomer of an Oral Small-Molecule TSH Receptor Agonist Exhibits Improved Pharmacologic Properties. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;7:105. Published 2016 Jul 27. doi:10.3389/fendo.2016.00105
- Vassart G, Pardo L, Costagliola S. A molecular dissection of the glycoprotein hormone receptors. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2004;29(3):119-126


