ML360 : LD (Lipid Droplet Formation) Inhibitor
ML360
Target Name
Lipid Droplet Formation
Target Alias
LD
Target Class
Lipid Storage Organelle
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of LD
Biological / Disease Relevance
Lipid Droplet Biogenesis, Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Cellular activity
3T3L1 LD assay (IC50)In vitro ADME
PAMPA permeability (10^-6 cm/sec)In vitro ADME
Mouse Plasma Stability (T1/2)Cellular activity
Cytotoxicity AssayTarget Information
Lipid droplets (LDs) are the universal lipid storage organelles (Kühnlein 2012, Farese 2009). Lipids remobilized from LDs are used both for energy production via beta-oxidation or anabolic reactions, such as membrane biosynthesis (Mak 2012, Zechner 2012, Winchester 2000). We have previously described three probes ML206, ML219, and ML220, which were optimized from high-throughput screening hits of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells and showed a potent LD reduction phenotype, with EC s of 8 nM, 2 nM, and 705 nM, respectively. Herein, we describe the further optimization of ML219 and characterization of the new probe, ML360. This compound showed potent inhibition of LD formation in the primary Drosophila melanogaster cell line as well as three mammalian cell lines (3T3-L1, COS-7, and AML12). It retained potent activity in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte to adipocyte differentiation conditions and showed no signs of cytotoxicity over this extended protocol unlike prior art compounds (AID 652183).
Properties

ML360
NCGC00345354
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 407.5 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N3O3 | |||
| cLogP | 4.4 | |||
| PSA | 65.4 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
CCOC1=C(OCC)C=C(CCNC(C2=CC=NN2CC3=CC(C)=CC=C3)=O)C=C1
InChI:
1S/C24H29N3O3/c1-4-29-22-10-9-19(16-23(22)30-5-2)11-13-25-24(28)21-12-14-26-27(21)17-20-8-6-7-18(3)15-20/h6-10,12,14-16H,4-5,11,13,17H2,1-3H3,(H,25,28)
InChIKey:
LFMLDXFGTVWZCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML360 (SID 161004695; CID 70789742) showed a potent LD reduction phenotype in Drosophila melanogaster S3 cells, simian COS-7 cells, and murine 3T3-L1 and AML12 cells. While the target for this probe is still unknown, we have shown that this chemotype inhibits the formation of LDs rather than increase the lipolysis of established LDs. The potent activity ML360 in mammalian cells makes it a worthwhile tool for biologists to use in studying the formation and biological role of LDs .
In vitro cellular activity - 3T3L1 LD accumulation assay
Summary /
Lipid droplet accumulation in mouse 3T3-L1 cells (AID 652180) showed dose response inhibition of ML360 (Figure 1A, green circle) but not with the negative control compound 1 (Figure 1B, blue circle). 3T3-L1 differentiation assay (AID 652183) showed dose response reduction of the lipid droplets (Figure 1B, blue square) without any cytotoxic effect as the cell number per treatment remained the same (Figure 1B, orange circle).
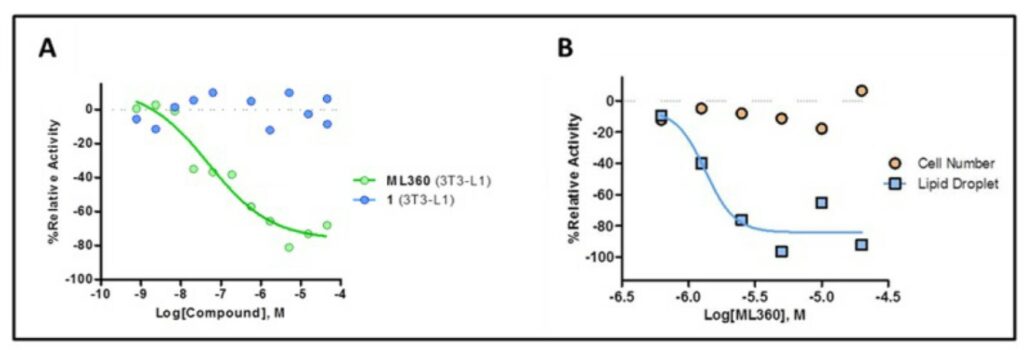
Figure 1. Cellular activity evaluation of the probe ML360
In vitro activity - ADME Profiling
| Compound | Solubility PBS buffer (pH 7.4) (μM) | PAMPA permeability (10 cm/sec) | Rat Liver Microsome Stability (T1/2) | Aqueous Glutathione Stability (96 hr) | PBS buffer (pH 7.4) Stability (48 hr) | Mouse Plasma Stability (T ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ML360 |
16 | 1518 | <5 min | > 99% | 99% | >60 min |
Summary /
Preliminary absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) profiling of ML360 demonstrated good stability in glutathione and PBS buffers for > 48 hr. Results also showed reasonable permeability and liver microsome stability.
References
- qHTS Assay for Lipid Storage Modulators: Summary
- Liu L, Zhang YQ, Tschapalda K, et al. ML360, A Potent Inhibitor of Lipid Droplet Formation. 2013 Apr 15 [Updated 2013 Nov 14]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010
- Kühnlein RP. Thematic review series: Lipid droplet synthesis and metabolism: from yeast to man. Lipid droplet-based storage fat metabolism in Drosophila. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(8):1430-1436. doi:10.1194/jlr.R024299
- Farese RV Jr, Walther TC. Lipid droplets finally get a little R-E-S-P-E-C-T. Cell. 2009;139(5):855-860. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.005
- Mak HY. Lipid droplets as fat storage organelles in Caenorhabditis elegans: Thematic Review Series: Lipid Droplet Synthesis and Metabolism: from Yeast to Man. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(1):28-33. doi:10.1194/jlr.R021006
- Zechner R, Zimmermann R, Eichmann TO, et al. FAT SIGNALS--lipases and lipolysis in lipid metabolism and signaling. Cell Metab. 2012;15(3):279-291. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.12.018
- Winchester B, Vellodi A, Young E. The molecular basis of lysosomal storage diseases and their treatment. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(2):150-154. doi:10.1042/bst0280150


