ML315 : CLK4 (Dual Specificity CDC-like Kinase 4) Inhibitor
ML315
Target Name
Dual Specificity CDC-like Kinase 4
Target Alias
CLK4
Target Class
Serine/ Threonine Protein Kinase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of CLK4
Biological / Disease Relevance
Cdc2-like (Clk) Kinases, mRNA Splicing, Splicing Modulator
In vitro activity
Clk4 bioassay (IC50)Target Information
The cdc2-like (Clk) kinases are critical elements of several important regulatory pathways involving pre-mRNA splicing. These kinases act by phosphorylating the serine- and arginine-rich (SR) proteins, which direct the early events of spliceosome assembly necessary for proper mRNA maturation. Mutations causing splicing defects have been linked to a number of disease processes, making the search for small-molecule regulators of enzymes associated with spliceosome function important for both the further study and potential treatment of these disorders. The dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated (Dyrk) kinases are associated with numerous cellular processes and disorders. In particular, overexpression of Dyrk1A may contribute to Down syndrome neuro-developmental abnormalities, and Dyrk1B/Mirk has been implicated in the cellular repair of cancer cells impaired by chemotherapy. Developing inhibitors of the Dyrk kinases would likely have important biochemical and therapeutic uses. Continuing in the search for selective inhibitors of Clk and Dyrk kinases, we now report a series of amino-substituted pyrimidines with excellent potencies against several Clk and Dyrk isoforms. The probe compound and its analogs have been subjected to Clk and Dyrk isoform selectivity profiling by Ambit Biosciences and three compounds have also been sent for KINOMEscan analysis to assess their selectivity in the context of the greater kinome. The reported compounds are low-nanomolar Clk and Dyrk inhibitors, with the most potent compound having IC s <10 nM against Clk1, Clk4, Dyrk1A, and Dyrk1B. The probe molecule (ML315) is a substituted aminopyrimidine and structurally distinct from previous quinazoline probes. ML315 (SID124950388; CID 46926514) should provide biochemical investigators with a new tool to be used in parallel with the quinazoline probes in efforts to determine which Clk and/or Dyrk isoforms are associated with particular biochemical events. Until isoform-selective inhibitors of each Clk and Dyrk kinase can be developed, parallel use of the available panel of inhibitors should enable biological investigations with these kinase families to proceed through a “process of elimination” approach.
Properties

ML315
NCGC00241342
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 374.2 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C18H13Cl2N3O2 | |||
| cLogP | 5.32 | |||
| PSA | 55.21 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 1440251-53-5 | |||
SMILES:
ClC1=CC(CNC2=NC=NC=C2C3=CC4=C(OCO4)C=C3)=CC(Cl)=C1
InChI:
1S/C18H13Cl2N3O2/c19-13-3-11(4-14(20)6-13)7-22-18-15(8-21-9-23-18)12-1-2-16-17(5-12)25-10-24-16/h1-6,8-9H,7,10H2,(H,21,22,23)
InChIKey:
JQSJAVBMIMDUFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
Post-transcriptional and post-translational processes are required to expand the 20,000–25,000 genes into the estimated 50,000–500,000 human protein variants. Alternate gene splicing is one mechanism by which this rich diversity of protein isoforms is achieved, and novel tools to help researchers understand and control gene splicing outcomes continue to be of considerable interest. Since the report of the first Clk inhibitor probe from this project (CID 44968231/ML167), there have been a limited number of reports on additional inhibitors of the Clk kinases. Each has a distinctive signature and ML315 represents a new chemotype with Clk activity and a unique structural and phamacological signature with which to interogate this complex process. Like the other inhibitors of this target, ML315 will be used to interrogate the role that the Clk kinases play in altering SR protein phosphorylation and the resulting consequences on gene splicing. Apart from Clk4 (inhibited by ML167), no selective inhibitors have been reported for the other Clk isoforms (Clk1- Clk3); published Clk inhibitors either potently inhibit more than one isoform or have not been tested against all four isoforms. Using the available panel of inhibitors, including ML315, in parallel would allow biological investigations involving these kinases to proceed until isoform-selective inhibitors become available. One approach to using the three probes in parallel is described here: Using previous probe ML167 in Assay 1, one can inhibit Clk4 (136 nM) and observe the effect. Using previous probe ML106 in Assay 2, one can inhibit Clk1, Clk4, and Dyrk1A (all <100 nM) and observe the effect. Phenotypic or biochemical differences between Assay 1 and Assay 2 could be attributed to the lack of Clk1 or Dyrk1A activity. Using the new probe (ML315) in Assay 3, one can potently inhibit Clk1 and Clk4 (<100 nM), while only moderately inhibiting Clk2 and Dyrk1A (>200 nM). Phenotypic or biochemical differences between Assay 2 and Assay 3 could be attributed to the lack of Clk1 activity, allowing the roles Clk1 and Dyrk1A to be further distinguished. The differences observed between Assay 2 and Assay 3 might also be the result of moderate Clk2 inhibition. The parallel use of these probes is further discussed in Section 4.1. The previously reported probe (ML167) has been requested by numerous researchers and we plan to offer ML315 to researchers alongside this agent. We have additionally made other Clk inhibitors from the literature and offer each to researchers in the hopes that off-target activities associated with the divergent poly-pharmacology of each chemotype will be mitigated by parallel assessment of the activity of multiple Clk inhibitors (Coombs 2010, Coombs 2013).
In vitro activity - Selectivity assay
| Bioassay | ML315 (IC50) |
|---|---|
|
Clk4 bioassay |
68 nM |
|
Clk1 (Anti-Target) |
68 nM |
|
Clk2 (Anti-Target) |
231 nM |
|
Clk3 (Anti-target) |
> 10,000 nM |
|
Dyrk1A |
282 nM |
|
Dyrk1B |
1156 nM |
Summary /
ML315 potently inhibit Clk1 and Clk4 while moderately inhibiting Clk2 and Dyrk1A. Selectivity determined across the kinome via profiling within KinomeScan (DiscoveRx, Reaction Biology). The probe was screened against 442 kinases. Additional activity was obsereved against Casein kinase 1 isoform epsilon (CSNK1E), Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP3K1), Serine/threonine-protein kinase PknB (PKNB), and protein kinase C epsilon (PRKCE).
In vitro activity - Pharmacokinetics profiling
Summary /
The in vitro pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of the probe (ML315) were profiled using a standard panel of assays (Table 1). The results from this profile suggested that ML315 has modest aqueous and assay media solubility, good permeability across an artificial membrane (PAMPA), good plasma stability but low microsomal stability. ML315 was also submitted for assessing off-target pharmacology using a Ricerca LeadProfiling® screen made up of 67 assays. The probe was assayed in duplicate at a concentration of 10 μM for all targets, and the following responses were noted as ≥ 50% inhibition or stimulation for biochemical assays (see Table 2).
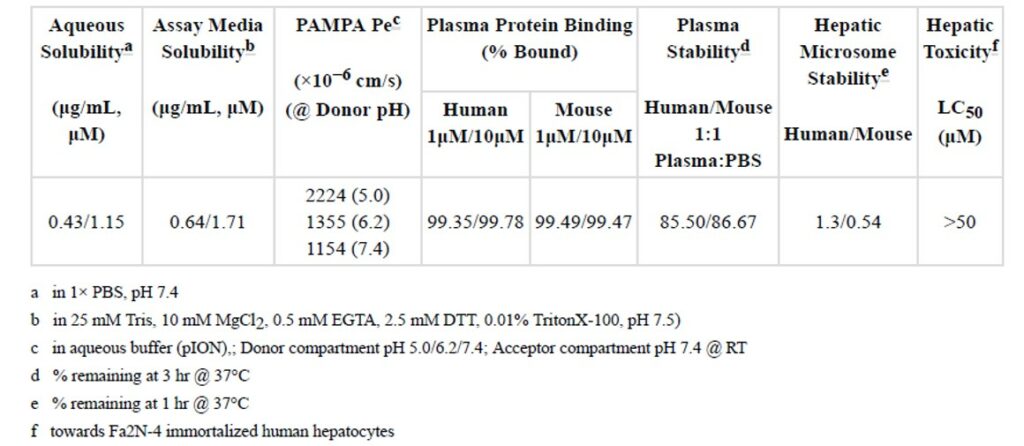
Table 1. Summary of in vitro ADME properties of ML315.
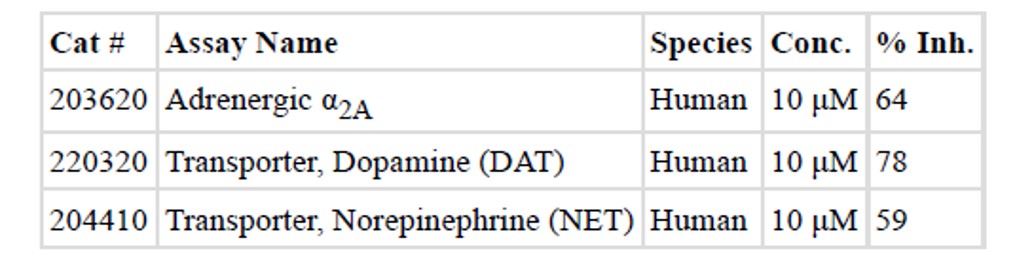
Table 2. Off-target pharmacology data for ML315 highlighting targets with ≥ 50% inhibition or stimulation.
References
- qHTS for Inhibitors of CDC-like Kinase 4: Summary
- Coombs TC, Tanega C, Shen M, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cdc2-like kinases 1 and 4 (Clk1, Clk4) 2012 Apr 16 [Updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK153503/
- Coombs TC, Tanega C, Shen M, et al. Small-molecule pyrimidine inhibitors of the cdc2-like (Clk) and dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated (Dyrk) kinases: development of chemical probe ML315. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23(12):3654-3661. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.096


