ML246 : PNC (Perinucleolar Compartment) Modulator
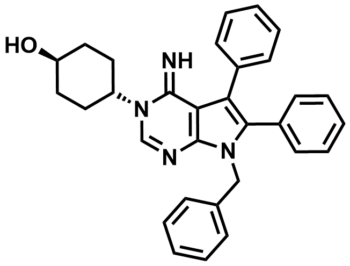
ML246
Target Name
Perinucleolar Compartment
Target Alias
PNC
Target Class
Subnuclear Body
Mechanism of Action
Modulator of PNC
Biological / Disease Relevance
Perinucleolar Compartment (PNC), Cancer Biology
In vitro activity
PNC Reduction (PC3M cells) (IC50)Cellular activity
Migration assay (IC50)Target Information
The perinucleolar compartment (PNC) is a subnuclear body found at the periphery of the nucleolus in the nucleus. Its function is not completely known yet, but it is a highly dynamic body that is enriched with Ribonucleic acid (RNA) transcripts and RNA-binding proteins. This compartment is highly prevalent in metastatic tumors and metastatically transformed cancer cell lines, making it a potential pan marker for metastatic progression. A high throughput, high content assay was developed to identify novel small molecules that reduce the prevalence of this metastasis biomarker in cancer cells. We have identified and further optimized a potent pyrrolopyrimidine series that reduces PNC prevalence in PC3M cells at submicromolar concentrations, where the cell viability is not affected. These compounds also show dose-dependent inhibition of migration and anchorage-independent growth in invasion and soft-agar assays, respectively. The probe candidate ML246, has drug-like physical properties and displays promising protein kinase, making it an ideal in vivo tool for establishing the link between the PNC and the metastatic transformation of tumor cells. ML246 will serve as a pivotal first step to further research the function of the PNC and its role in cancer metastasis.
Properties

ML246
Metarrestin
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 474.6 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C31H30N4O | |||
| cLogP | 5.6 | |||
| PSA | 64.6 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 1443414-10-5 | |||
SMILES:
O[C@@H]1CC[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(C2=N)C(C4=CC=CC=C4)=C(C5=CC=CC=C5)N3CC6=CC=CC=C6)CC1
InChI:
1S/C31H30N4O/c32-30-28-27(23-12-6-2-7-13-23)29(24-14-8-3-9-15-24)34(20-22-10-4-1-5-11-22)31(28)33-21-35(30)25-16-18-26(36)19-17-25/h1-15,21,25-26,32,36H,16-20H2
InChIKey:
WSMXAUJFLWRPNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
The prevention and treatment of cancer metastasis is a prominent unmet medical need. Several molecular targets have been identified and explored for inhibition of the metastatic process, but these approaches have not yet yielded success in the clinic. The perinucleolar compartment (PNC) is a multicomponent subnuclear structure that is highly prevalent in metastatic tumors (Kamath 2005, Slusarczyk 2010). Here, we present the discovery of ML246 (SID 117695978; CID 50985821), a probe molecule that is able to disrupt the assembly of PNC in a metastatically transformed prostate cancer cell line without overt cytotoxicity. This structural class also impacts in vitro migration of tumor cells, making it useful for advanced cell-based studies. The probe displays promising in vitro ADME properties and in vivo mouse pharmacokinetics, making it an ideal candidate for understanding the therapeutic value of PNC disruption as a novel approach towards combating metastasis in cancer treatment.
Cellular activity - Selectivity and Cytotoxicity Assay
| Bioassay | ML246 (IC50) |
|---|---|
|
PNC Reduction |
0.397 uM |
|
PC3M cells ATP assay (Cytotoxicity) |
9.960 uM |
Summary /
Extensive SAR explorations yielded a probe molecule ML246 that is able to reduce the PNC population in PC3M cells at sub-micromolar concentrations with cytotoxicity observed at ~10μM (25-fold selectivity). The probe shows ~10-fold selectivity between growth inhibition and cytotoxicity in the NCI-60 panel. Thus the chemical series represents first-in-class molecules that reduce the prevalence of the PNC and do not operate via known cytotoxic mechanisms.
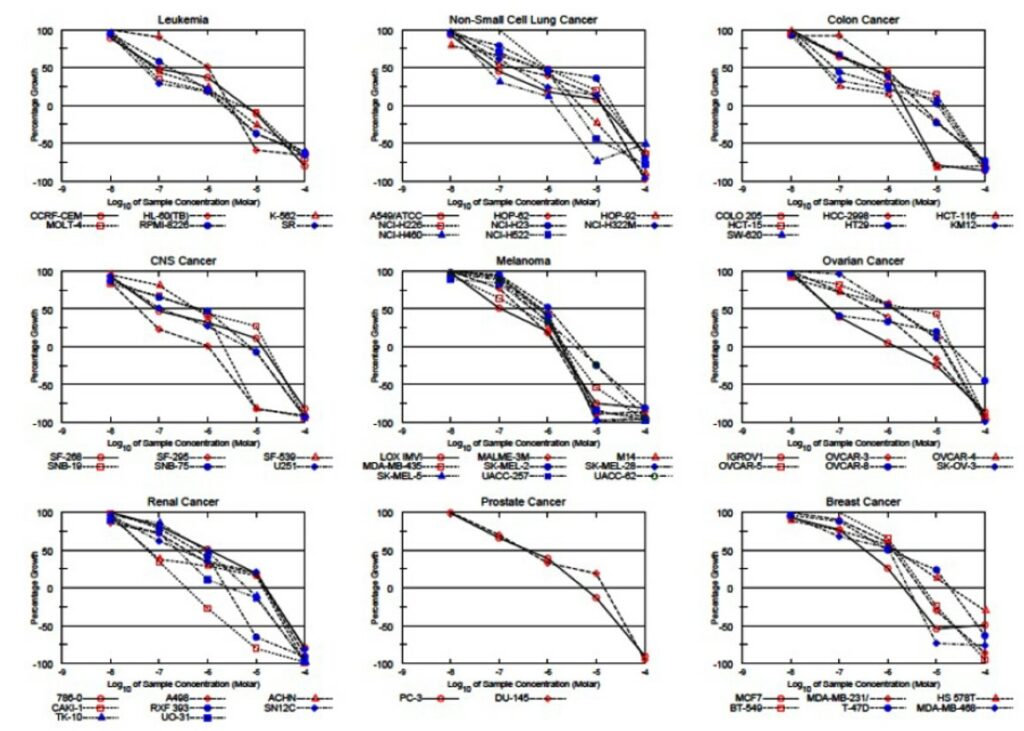
Figure 1. NCI-60 panel: Dose response growth inhibition curves for ML246 in 60 cancer cell lines. The curves are grouped according to the type of cancer. Concentrations able to produce a percentage of growth below zero indicate loss of cell density and can be correlated to cell death.
Cellular activity - Functional assay: Proliferation and invasion assay
Summary /
After activity optimization in the PNC assay, it was necessary to examine if these compounds had an effect on migration. Table 1 summarizes preliminary results obtained in an invasion assay with ML246.

Table 1. BellBrook Labs Proliferation and Migration Data for ML246 and an inactive control.
Cellular activity - Functional assay: 3D PC3M soft agar assay
Summary /
An examination of the number of cells that have invaded through the 3D collagen channel reflects their migratory aptitude. Gratifyingly, the novel PNC-reducer probe ML246 showed dose dependent inhibition of migration with IC s 3–4 μM. The numbers of cells in the output port after the assay duration were also counted as a measurement of proliferation. Here too, the probe showed dose-dependent inhibition activity, suggesting that the anti-invasive effect of the compound is concomitant with an anti-proliferative effect.

Figure 2. (A) Histogram representing number and size (μm) of PC3M soft agar colonies after 14 days treatment with ML246 at 3.8 and 18.6 nM. (B) Representative images of colonies at these concentrations.
In vitro activity - PDSP comprehensive binding panel
Summary /
ML246 is a novel chemical entity and has no previously disclosed interactions with biological targets. The probe has been screened against 44 GPCR and CNS relevant targets in the PDSP comprehensive binding panel. With the exception of the sigma 2 receptor, ML246 was mostly inactive against all these targets. Notably, this includes dopaminergic activity, as the original hit was found to be an allosteric D1 agonist in PubChem AID 504660.
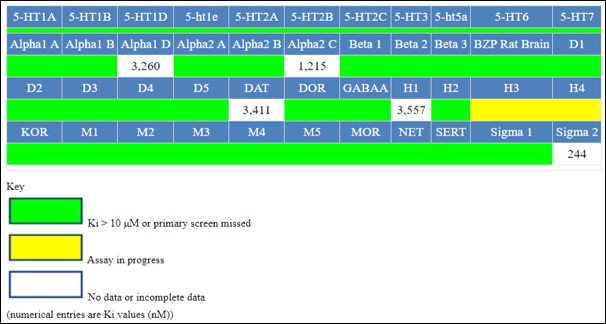
Table 2. Profiling of the probe, ML246, in the PDSP comprehensive panel.
In vitro and vivo activity - ADME and PK profiling
Summary /
ML246 has good stability in PBS buffer. It also has good stability in mouse plasma and is not rapidly metabolized by mouse liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH. At a 50 mpk high dose, the probe provided significant in vivo exposure in mice, with a C max of 20.3 μM @ 30 min and a C last of 1.3 μM @ 48 hrs. Some mortality was observed (3/18), but this is expected, as the exposure is well beyond the expected therapeutic levels. Subsequent experiments with 25 mpk intraperitoneal (IP) dosing provided very good exposure without any sign of toxicity.
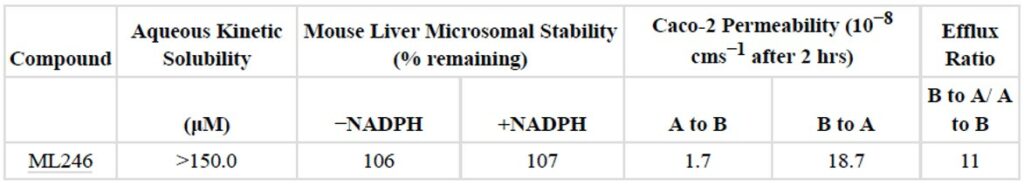
Table 3. In vitro ADME data for ML246.
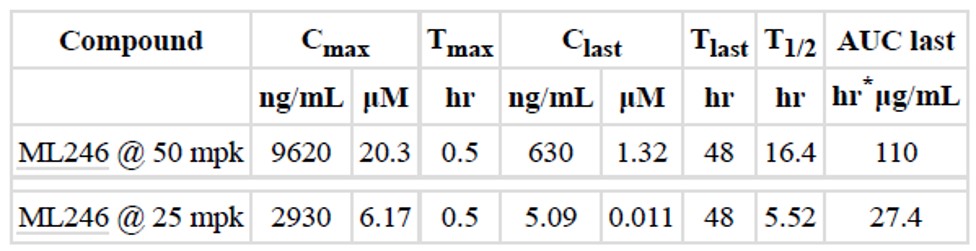
Table 4. Comparison of Mouse Pharmacokinetics Parameters of Probe after IP Dosing of 50 or 25 mpk in Male C57BL/6 Mice.
References
- PubChem link: High Content Assay for Compounds that inhibit the Assembly of the Perinucleolar Compartment: Summary
- Frankowski K, Patnaik S, Schoenen F, et al. Discovery and Development of Small Molecules That Reduce PNC Prevalence. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010.
- Kamath RV, Thor AD, Wang C, et al. Perinucleolar compartment prevalence has an independent prognostic value for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(1):246-253.
- Slusarczyk A, Kamath R, Wang C, et al. Structure and function of the perinucleolar compartment in cancer cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:599-605. doi:10.1101/sqb.2010.75.026


