ML156 : GBA (Glucocerebrosidase (N370S mutant)) Modulator

ML156
Target Name
Glucocerebrosidase (N370S mutant)
Target Alias
GBA
Target Class
Hydrolases
Mechanism of Action
Modulator of GBA
Biological / Disease Relevance
Gaucher; ER-lysosomal trafficking; chaperone of glucocerobrosidase
In vitro activity
N370S GC bioassay (IC50)Cellular activity
Chaperone activity assay (IC50)Target Information
Known glycosidase chaperone molecules belong to the aminosugar class. Because iminosugar inhibitors work by mimicking the transition state of the glycosidic cleavage, they tend to be poorly selective. This has hampered their advance in clinical development. Alternative scaffolds with chaperone activity are quite desirable. Here, we present a new non-aminosugar series of glucocerebrosidase inhibitors having chaperone capacity.
Properties

ML156
NNC 26-9100
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 556.3 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C22H25BrCl2N6S | |||
| cLogP | 5.3 | |||
| PSA | 101 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 199522-35-5 | |||
SMILES:
ClC1=C(Cl)C=C(CN(C2=NC=C(Br)C=C2)CCCNC(NCCCC3=CNC=N3)=S)C=C1
InChI:
1S/C22H25BrCl2N6S/c23-17-5-7-21(29-12-17)31(14-16-4-6-19(24)20(25)11-16)10-2-9-28-22(32)27-8-1-3-18-13-26-15-30-18/h4-7,11-13,15H,1-3,8-10,14H2,(H,26,30)(H2,27,28,32)
InChIKey:
UREJDUPKGMFJRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML156 (CID 9893924, SID 89449177), is able to inhibit the hydrolytic activity of the N370S mutant form of glucocerebrosidase. Most importantly, ML156 increased glucocerebrosidase translocation to the lysosome in Gaucher patient-derived fibroblasts homozygous for the N370S mutation, and can be used to study ER-lysosomal trafficking of clinically relevant GC mutants in vitro. This probe may be a useful lead for the pre-clinical development of a chemical chaperone of glucocerebrosidase.
In vitro activity - Selectivity
| Bioassay | ML156 (IC50) |
|---|---|
|
N370S GC |
0.58 uM |
|
Chaperone activity (N370S GC fibroblast) |
0.50 uM |
|
Alpha-glucosidase (Anti-Target) |
> 57 uM |
|
Alpha-galactosidase (Anti-Target) |
> 57 uM |
Summary /
ML156 is found to have > 100 fold selective against glucocerebrosidase.
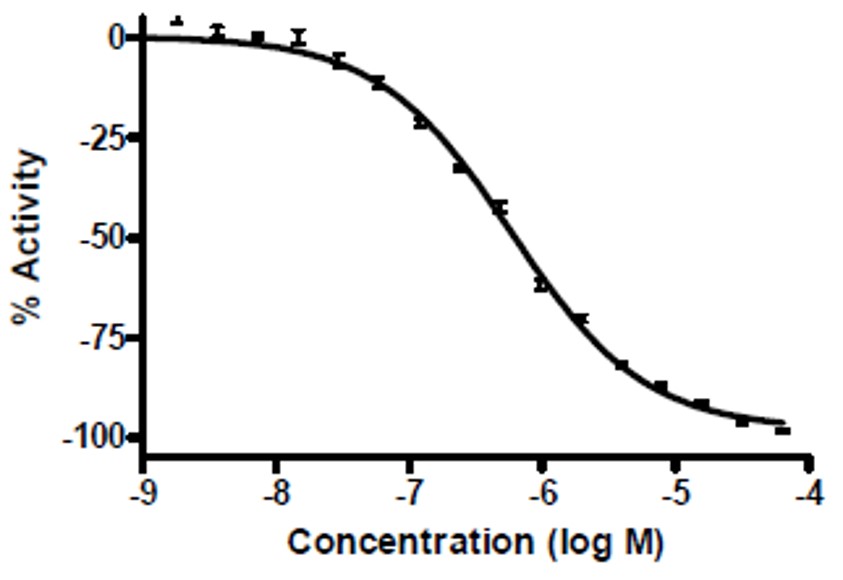
Figure 1. Concentration-response of ML156, in primary screening assay for N370S GC inhibition from tissue homogenate. Compound IC50, measured in triplicate on three different days, was 580 +/- 30nM.
Cellular activity - Chaperone assay
Summary /
To demonstrate chaperone activity, the capacity of ML156 and ML155 to increase the translocation of GC to the lysosome was measured (8, 16, 30, 31). In this experiment, wildtype and mutant fibroblasts were incubated for five days with compound 8i, followed by cell fixation and staining with a selective fluorescent GC antibody. Compounds able to promote trafficking from the ER to the lysosome increased the fluorescent lysosomal signal. DMSO and isofagomine were used as negative and positive controls. Figure 2 shows the increment of signal in both cell lines that resulted from treatment, confirming the chaperone capacity of these compounds.
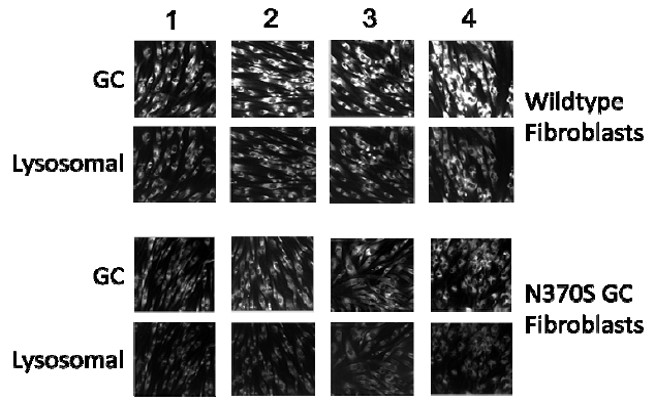
Figure 2: Chaperone activity of compound 13, NCGC00182292 (CID 40225210), and others using wildtype and homozygous, mutant N370S GC fibroblasts. Two genotypes of fibroblasts, fibroblasts homozygous for wildtype GC (top) and fibroblasts homozygous for N370S GC (bottom) were stained both with a Cy3-labeled antibody for GC protein content (first row) and a FITC-labeled antibody specific for lysosomal compartments (LAMP1; second row) after treatment with (1) DMSO vehicle, (2) 10μM Isofagomine (CID 447607), (3) 10μM compound 13, NCGC00182292 (CID 40225210), and (4) 1μM NCGC00159568 (CID 9893924). Several compounds, including isofagomine (CID 447607) and compound 13, NCGC00182292 (CID 40225210), show increased lysosomal GC protein after treatment.
In vitro and vivo activity - ADME and PK Profiling
Summary /
The result of a microsomal stability study of ML156 (CID9893924) is shown in Table 1. After incubation of the molecule in mouse liver microsomes for 60 minutes in the present of NADPH, 58% of the molecule remained, this suggested that ML156 has a reasonable microsomal stability. In addition, the pharmacokinetic profiles of ML156 in male Swiss Albino mice after intraperitoneal administration twice at a 12 hour interval of the probe at 20mg/kg dose are shown in Table 2. This probe has demonstrated chaperone activity, and preliminary pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that the molecule has good exposure in plasma, brain and liver upon IP administration. Exposure in brain is especially significant, as the current standard-of-care, enzyme replacement therapy, has no effect on the neurological component of the disease. In addition, at this high dose, the compound did not exhibit any acute toxicity in initial testing.
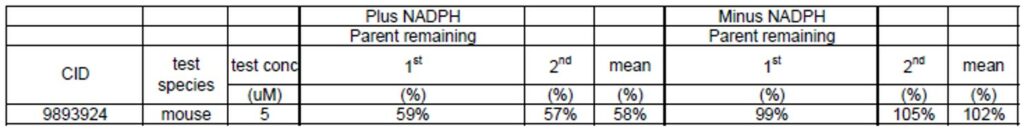
Table 1. Mouse microsomal stability assay at 60 minutes.
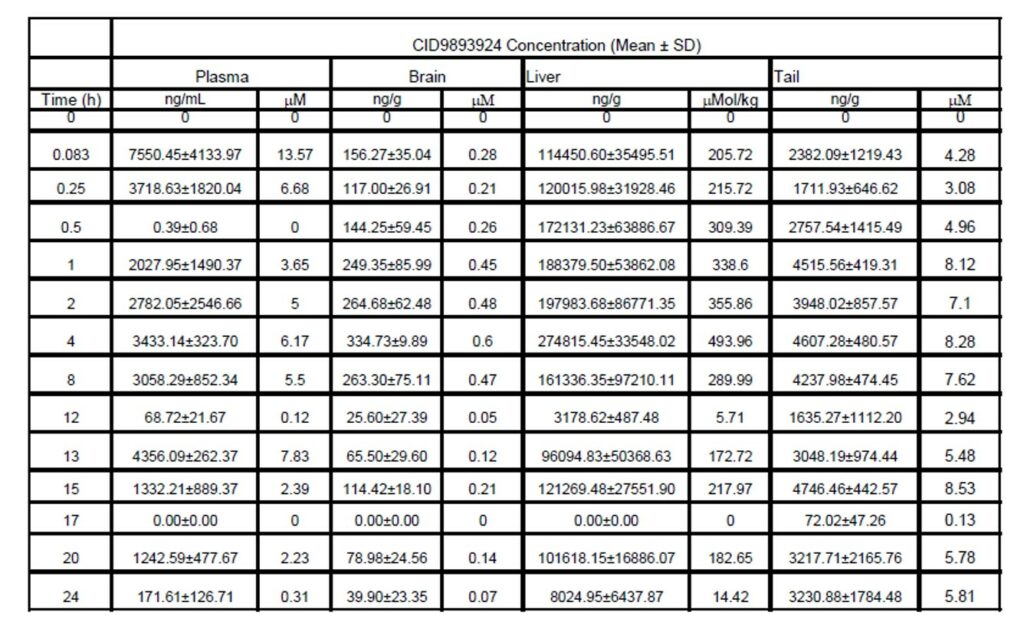
Table 2. Concentrations of ML156 / CID9893924 in plasma, brain, liver and tail; intraperitoneal administration twice at a 12 hour interval of ML156 / CID9893924 at 20mg/kg dose in male Swiss Albino Mice (mean and SD).
References
- PubChem link: qHTS Assay for Inhibitors and Activators of N370S glucocerebrosidase as a Potential Chaperone Treatment of Gaucher Disease: Summary
- Motabar O, Huang W, Marugan JJ, et al. Identification of Modulators of the N370S Mutant Form of Glucocerebrosidase as a Potential Therapy for Gaucher Disease - Chemotype 2. 2010 Mar 24 [Updated 2011 Mar 25]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56229/
- Lieberman RL, Wustman BA, Huertas P, Powe AC Jr, Pine CW, Khanna R, Schlossmacher MG, Ringe D, Petsko GA. Structure of acid beta-glucosidase with pharmacological chaperone provides insight into Gaucher disease. Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Feb;3(2):101-7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio850. Epub 2006 Dec 24. PMID: 17187079


