ML002 : sPrx2 (S. mansoni Peroxiredoxins) Inhibitor
ML002
Target Name
S. mansoni Peroxiredoxins
Target Alias
sPrx2
Target Class
Oxidoreductase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of sPrx2
Biological / Disease Relevance
Redox Balance in Schistosomes, Scistosomiasis
In vitro assay
IC50In vitro assay
S. mansoniIn vivo assay
Mouse ModelInactive Control
Available
Target Information
Schistosoma mansoni, a causative agent of schistosomiasis, reside in the bloodstream of their host up to 30 years without being eliminated by the host immune attack. One proposed survival mechanism is the production of an antioxidant “firewall” that neutralizes the oxidative assault of the host’s immune attack. Schistosoma mansoni peroxiredoxins (Prx) are important parasite antioxidant proteins that play a crucial role in redox balance mechanisms. Inhibition of Prx activity was screened in a coupled-enzyme format with reducing equivalents being transferred from NADPH to glutathione intermediate via thioredoxin/glutathione reductase (TGR)-catalyzed reaction, then from thioredoxin to hydrogen peroxide via Prx-catalyzed electron transfer. A decrease in the fluorescence intensity of NADPH was used to measure the enzyme activity.
Properties

ML002
NCGC00015800
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 187.15 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C9H5N3O2 | |||
| cLogP | 1.8 | |||
| PSA | 75.3 A^2 | |||
| Storage | 2-8 | |||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | ||||
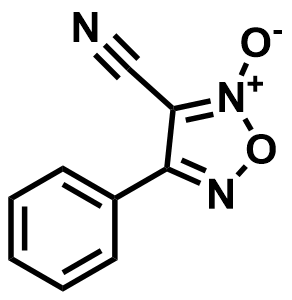
SMILES:
N#CC1=[N+]([O-])ON=C1C2=CC=CC=C2
InChI:
InChI=1S/C9H5N3O2/c10-6-8-9(11-14-12(8)13)7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5H
InChIKey:
PMYJGTWUVVVOFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML002 (CID 1756, SID 11111612) is identified as a selective inhibitor of the proteins involved in Schistosoma mansoni redox reaction, in particular the Peroxiredoxins and the Thioredoxin glutathione reductase with IC50 of 9 uM. This probe compound has been screened against 81 PubChem bioassays but only showed activity to 8 bioassays. Moreover, ML002 is observed to be inactive at 50 uM against the human glutathione reductase (GR, an essential enzyme in the mammalian redox cascade) and against the S. mansoni LDH suggesting a selective compound.
In vitro activity
| S. mansoni Prx/TGR Assay (IC50) | human GR Counterscreen | S. mansoni LDH Counterscreen | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NCGC00015800 (ML002) |
9 uM | Inactive | Inactive |
In vitro Parasitic Assay
| S. mansoni Toxicity Assay | |
|---|---|
|
NCGC00015800 (ML002) |
10 uM |
Summary /
Compounds were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and added at concentrations indicated to freshly perfused worms in RPMI 1640 containing 25 mM HEPES, pH 7, 150 units/ml penicillin, 125 mg/ml streptomycin and 10% FCS (Cell Grow, Fisher). Media were replaced every 2 d with fresh media with the compounds added at the designated concentrations. Control worms were treated with equal amounts of DMSO alone. Worms were subsequently observed for motility and mortality and collected at the indicated times for analysis. Worms were homogenized by sonication in PBS, and homogenates were assayed for enzyme activities as described. To assess the importance of NO production, the potassium salt of 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide (carboxy-PTIO, Invitrogen), a NO scavenger, was dissolved in water and incubated with freshly perfused S. mansoni worms at 100 mM in the presence or absence of 10 mM SID 11111612.
Results showed 100% inhibition of parasitic survival after 24 hours. The anti-schistosomal activity of ML002 is concomitant with NO production; however, other unrelated NO donors did not have an effect against Schisto worms.
Mouse Model
| Compound | Mouse Model |
|---|---|
|
ML002 |
10 mpk |
Summary /
ML002 was dissolved in DMSO and administrated by intraperitoneal injection at 10 mg/kg (mpk) daily for five consecutive days during the development of S.mansoni in the mouse. Large and highly significant reductions in worm burdens were observed from 3 experimental treatments: (1) skin/lung stage larvae; (2) juvenile liver-stage worm; (3) adult egg-laying parasite. A DMSO treated infected mice was used as a control.
Results showed that worms recovered from treatment 2 are small and stunted (specially males) relative to the worms recovered from untreated mice. Gross anatomy of the liver from the ML002 treated mice showed decrease liver granuloma resulting from host immunological reaction against trapped parasite eggs.
References
- A furoxan–amodiaquine hybrid as a potential therapeutic for three parasitic diseases
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen Identifies Inhibitors of the Schistosoma mansoni Redox Cascade
- Identification of oxadiazoles as new drug leads for the control of schistosomiasis
- Structure mechanism insights and the role of nitric oxide donation guide the development of oxadiazole-2-oxides as therapeutic agents against schistosomiasis


