ML092 : Cruzain (T. cruzi Cruzipain) Inhibitor
ML092
Target Name
T. cruzi Cruzipain
Target Alias
Cruzain
Target Class
Cysteine Endopeptidase
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of Cruzain
Biological / Disease Relevance
Anti-trypanosomal agent, Chagas disease
In vitro activity
Cruzain IC50Inactive Control
Available
Target Information
Cruzain is a key cysteine protease in Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi); it is essential for the parasite survival and replication, and has been validated as a drug target for this organism. Trypanosoma cruzi, a protozoan parasite, is the causative agent of Chagas disease. This is a major neglected tropical disease affecting over 16 million people, primarily in Central and South America. Discovering novel inhibitors of cruzain and determining their enzyme-bound structures is expected to provide a platform for drugdiscovery efforts against this resistance target.
Project Team
Properties

ML092
Cruzain-IN-1
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 300.27 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C14H10F2N6 | |||
| cLogP | 2.5 | |||
| PSA | 79.4 A^2 | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | 10 mM in DMSO | |||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
CCN1C=NC2=C(N=C(C#N)N=C12)NC3=CC(F)=CC(F)=C3
InChI:
InChI=1S/C14H10F2N6/c1-2-22-7-18-12-13(20-11(6-17)21-14(12)22)19-10-4-8(15)3-9(16)5-10/h3-5,7H,2H2,1H3,(H,19,20,21)
InChIKey:
SZYYBVWPURUFRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML092 (CID 44143088; SID 99206571; Cruzain-IN-1) exhibits potent near-stoichiometric inhibition of Cruzain and should be useful as both a potent effector of the enzyme in vitro and as a starting point for development of anti-trypanosomal agents. The majority of current advanced cruzain inhibitors act via irreversible covalent inhibition, such as the probe detailed within. Our probe acts via reversible covalent inhibition, and to the best of our knowledge, we provide the first co-crystallization of nitrile-based inhibitor to cruzain.
This probe displays potent (~200 pM) reversible covalent inhibition of both cruzain and rhodesian (two homologous cysteine proteases) via nucleophilic attack of the active site cysteine moiety onto the nitrile group on the probe molecule.
ML092 is soluble at 10 mM in DMSO. The compound is not fluorescent with blue excitation wavelengths (~340 nm). Solubility in buffer has not been determined.
In vitro activity - Selectivity Assay
| ML092 (IC50) | |
|---|---|
|
Cruzain qHTS |
100 nM |
|
Rhodesain |
< 6 nM |
|
TbCatB |
28000 nM |
|
Papain Counterscreen |
300 nM |
|
Cruzain - Secondary Cuvette Assay |
0.2 nM |
Summary /
Papain, another cysteine protease (related to cruzain) known to utilize the same Z-FR-AMC fluorogenic substrate, was selected as a convenient profiling target to determine selectivity of the probe. ML092 is 3 fold more selective against Cruzain than against Papain.
In vitro activity - Kinase Activity Panel (Reaction Biology)
Summary /
Kinase Activity Panel showed that ML092 and analogs preferentially hit the cathepsin proteases, however cathepsins are located in the lysosomes of cells whereas parasites are located in the more accessible cytoplasm.
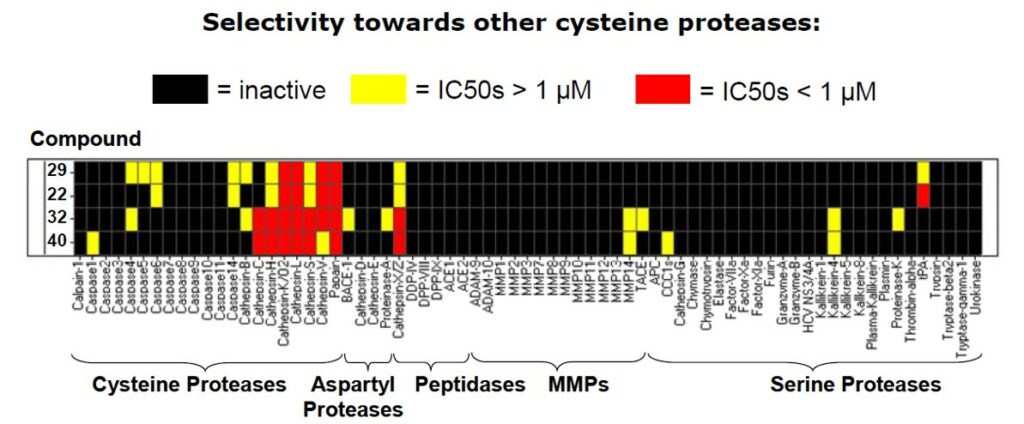
Figure 1. Comparative data showing probe specificity for different kinase targets.
In vitro activity - Co-crystallization
Summary /
Co-crystallization of the probe molecule with cruzain seems to indicate that the N9 substituent is exposed to solvent and could be utilized to improve pharmacokinetic properties (i.e. solubility and cell permeability). Co-crystallization also helps explain the observation that larger/hydrophobic groups off the aniline are unfavorable. The S2 binding pocket is fairly narrow and can not accommodate larger groups.
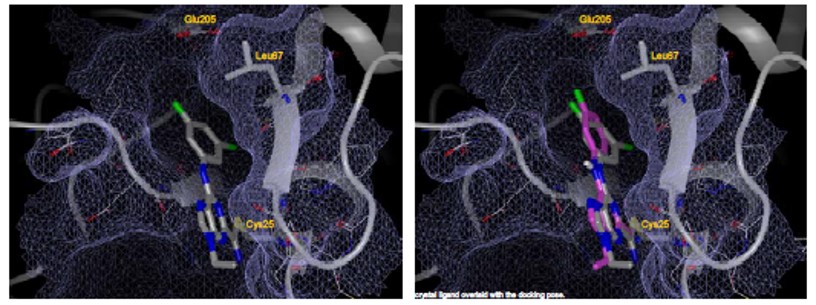
Figure 2. Co-crystallization of probe molecule with cruzain-docking pose (A). Docking pose (purple) overlaid with co-crystal structure (grey) (B).
References
- Probe Development Summary of Inhibitors of Cruzain
- Probe Development Summary of Promiscuous Inhibitors (Artifacts) of Cruzain
- Mott BT, Ferreira RS, Simeonov A, Jadhav A, Ang KK, Leister W, Shen M, Silveira JT, Doyle PS, Arkin MR, McKerrow JH, Inglese J, Austin CP, Thomas CJ, Shoichet BK, Maloney DJ. Identification and optimization of inhibitors of Trypanosomal cysteine proteases: cruzain, rhodesain, and TbCatB. J Med Chem. 2010 Jan 14;53(1):52-60. doi: 10.1021/jm901069a. PMID: 19908842; PMCID: PMC2804034
- Luci D, Lea W, Ferreira R, et al. Reversible and non-covalent benzimidazole-based in vivo lead for Chagas disease. 2011 Apr 15 [Updated 2013 Feb 28]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK133417/
- Simeonov, A.; Jadhav, A.; Thomas, C. J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Southall, N. T.; Shinn, P.; Smith, J.; Austin, C. P.; Auld, D. S.; Inglese, J. Fluorescence spectroscopic profiling of compound libraries. J Med Chem 2008, 51, 2363-71
- Feng, B. Y.; Simeonov, A.; Jadhav, A.; Babaoglu, K.; Inglese, J.; Shoichet, B. K.; Austin, C. P. A high-throughput screen for aggregation-based inhibition in a large compound library. J Med Chem 2007, 50, 2385-90
- Inglese, J.; Auld, D. S.; Jadhav, A.; Johnson, R. L.; Simeonov, A.; Yasgar, A.; Zheng, W.; Austin, C. P. Quantitative high-throughput screening: a titration-based approach that efficiently identifies biological activities in large chemical libraries. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci.USA 2006, 103, 11473-8
- Palmer, J. T.; Rasnick, D.; Klaus, J. L.; Bromme, D. Vinyl Sulfones as Mechanism-Based Cysteine Protease Inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1995, 38, 3193-3196
- Roush, W. R.; Gwaltney, S. L.; Cheng, J.; Scheidt, K. A.; McKerrow, J. H.; Hansell, E. Vinyl Sulfonate Esters and Vinyl Sulfonamides: Potent, Irreversible Inhibitors of Cysteine Proteases. J Am Chem Soc 1998, 120, 10994-10995


