ML079 : NPSR1 (Neuropeptide-S Receptor) Antagonist
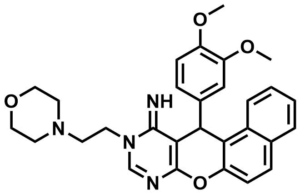
ML079
Target Name
Neuropeptide-S Receptor
Target Alias
NPSR1
Target Class
G-protein Coupled Receptor
Mechanism of Action
Antagonist of NPSR1
Biological / Disease Relevance
cAMP and calcium signaling pathways stimulated by NPS, Sleep and anxiety disorder
In vitro activity
NPSR1 cAMP IC50In vitro activity
[125I]Y10-hNPS displacement IC50Target Information
Neuropeptide S receptor (NPSR), previously known as GPR154, is a recently deorphanized G protein coupled receptor. Its endogenous ligand is the 20 amino acid peptide Neuropeptide S (NPS). Activation of NPSR induces transient increases in intracellular calcium and cAMP, suggesting coupling of this receptor to both Gs and Gq G proteins. NPS and its receptor are found in various tissues. The receptor is highly expressed in brain areas that have been implicated in modulation of arousal, stress and anxiety. Central administration of NPS in mice produces an unusual profile of activity by inducing wakefulness and arousal, while at the same time suppressing anxiety (Xu, 2004).
Project Team
Properties

ML079
LSM-1924
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 498.573[g/mol] | |||
| Molecular Formula | C29H30N4O4 | |||
| cLogP | 3.6 | |||
| PSA | 79.6 | |||
| Storage | ML079 is a white powder at room temperature, chemically stable and with no apparent reactivity with air. | |||
| Solubility | ML079 is a very lypophilic compound ease to dissolve in organic solvents such us MeOH, Cl2CH2 or acetone. | |||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
COC1=C(OC)C=C(C2C3=C4C=CC=CC4=CC=C3OC(N=CN5CCN6CCOCC6)=C2C5=N)C=C1
InChI:
InChI=1S/C29H30N4O4/c1-34-22-9-8-20(17-24(22)35-2)25-26-21-6-4-3-5-19(21)7-10-23(26)37-29-27(25)28(30)33(18-31-29)12-11-32-13-15-36-16-14-32/h3-10,17-18,25,30H,11-16H2,1-2H3
InChIKey:
HTAQOIIMDZRODK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML079 (SID 56431665; CID 3719993) exhibits functional antagonism equally for cAMP and intraceullar calcium signaling pathways stimulated by NPS in the cell-based assays, as opposed to the only other reported antagonist of NPS, SHA68, which selectively inhibits calcium signaling. The complete blockade of both cAMP and calcium signaling pathways may be necessary to fully antagonize NPSR1 function in animal models. As such, this probe should be used as a research tool to further study the functions of NPS receptor ex vivo and in animal models.
In vitro activity - Selectivity and Validation assays
| ML079 | SHA 68 | |
|---|---|---|
|
NPSR1 |
1.585 uM | |
|
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 (Anti-Target) |
> 100 uM | |
|
[125I] NPS Displacement |
0.256 uM | 0.006 uM |
|
NPSR1, cAMP IC50 |
2.99 uM | 0.583 uM |
|
NPSR1, Calcium Mobilization IC50 |
2.67 uM | 0.029 uM |
|
Functional Selectivity for C++: cAMP |
1:1 | 20:1 |
Summary /
ML079 is observed to be equally potent in the cAMP and calcium functional assays, antagonizing both biological pathways. In contrast, SHA68 has a 20 times selectivity towards calcium activation than cAMP activation. This could explain that while more potent in the radioligand experiment, SHA68 only partially blocked NPS-induced activity when injected at 50 mg/kg i.p. (Okamura, 2008). This dosing yielded single-digit micromolar concentrations in brain.
It is observed that activation of NPSR induces transient increases in intracellular calcium and cAMP, suggesting coupling of this receptor to both Gs and Gq G proteins. It can be hypothesized then that antagonism of NPS stimulation would require functional antagonism of either cAMP or both cAMP and calcium signaling. ML079 could provide a means of testing this hypothesis because this compound does not appear to be functionally selective for one pathway or the other.
References
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen for Antagonists of the Neuropeptide S Receptor: Summary
- Marugan J, Liu K, Zheng W, et al. Identification of Functionally Selective Small Molecule Antagonists of the Neuropeptide-S Receptor: Naphthopyranopyrimidines. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010
- Okamura, N., Habay, S.A., Zeng, J., Chamberlin, A.R. and Reinscheid, R.K. (2008) Synthesis and pharmacological in vitro and in vivo profile of 3-oxo-1,1-diphenyltetrahydro- oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine-7-carboxylic acid 4-fluoro-benzylamide (SHA 68), a selective antagonist of the neuropeptide S receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325 (3), 893-901
- Xu, Y.L., Reinscheid, R.K., Huitron-Resendiz, S., Clark, S.D., Wang, Z., Lin, S.H., Brucher, F.A., Zeng, J., Ly, N.K., Henriksen, S.J., de Lecea, L., Civelli, O. (2004) Neuropeptide S: a neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 43 (4), 487-97


