ML170 : PKM (Pyruvate Kinase M2) Activator
ML170
Target Name
Pyruvate Kinase M2
Target Alias
PKM
Target Class
Kinase
Mechanism of Action
Activator of PKM
Biological / Disease Relevance
Metabolism, Cancer Metabolism
In vitro activity
hPyk-M2 bioassay (EC50)In vitro activity
LDH Secondary Assay (EC50)Target Information
The expression of human pyruvate kinase M2 (hPK-M2) in cancer cells appears to be critical for tumor cell growth and proliferation in vivo. Because the PK-M2 isoform is expressed in all cancer cells studied, it represents a target for drug development that could potentially enable tumor cells to return to a normal state of metabolism. If this novel strategy for targeting malignancy were successful, it would be applicable to diverse types of cancer. The probe ML170 (CID-4547230) is a member of a series of highly specific allosteric activators for the tumor-specific isoform of human pyruvate kinase (M2 isoform). The probe affects the cooperativity of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) binding, with little affect on adenosine diphosphate (ADP) binding, in a manner similar to Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP).
Project Team
Properties

ML170
NCGC00185939
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 330.4 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C17H18N2O3S | |||
| cLogP | 2.3 | |||
| PSA | 83.6 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 899717-26-1 | |||
SMILES:
CC1=C(C)C=C(NS(=O)(C2=CC3=C(NC(CC3)=O)C=C2)=O)C=C1
InChI:
InChI=1S/C17H18N2O3S/c1-11-3-5-14(9-12(11)2)19-23(21,22)15-6-7-16-13(10-15)4-8-17(20)18-16/h3,5-7,9-10,19H,4,8H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)
InChIKey:
SNFROMRRGGKYTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
In vitro activity - Selectivity Assays
| ML170 (EC50) | |
|---|---|
|
hPyk-M2 |
163 nM |
|
LDH kinetic assay |
146 nM |
|
hPyk-M1 |
Inactive |
|
hPyk-R |
Inactive |
|
hPyk-L |
Inactive |
Summary /
ML170 is observed to be selective and potent (with > 100 fold selectivity) against hPyk-M2. This probe is also active in the confirmatory LDH assay; a kinetic mode assay generated by coupling the generation of pyruvate by pyruvate kinase to the depletion of NADH through lactate dehydrogenase. It is found to be inactive against the human Reticulocyte Pyruvate Kinase (hPyk-R), Pyruvate Kinase M1 Isoform (hPyk-M1), and Liver Pyruvate Kinase (hPyk-L).
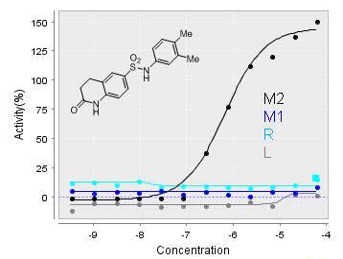
Figure 1. Dose response curves for NCGC00185939/ CID_4547230/ ML170 against the four hPyk isozymes.
In vitro assay - Mechanism of Action Studies
Summary /
The mode of action for the probe versus hPykM2 is assessed through analysis of the steady-state kinetics of PEP and ADP by the hPykM2. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is known to allosterically activate hPykM2 through induction of an enzyme state with a high affinity for PEP. In the absence of any of these activators, hPyk shows low affinity for PEP (KM ~ 1.5mM). In the presence of NCGC00031955 (CID_654376, SID_851783) or NCGC00030335 (CID_650361, SID_847943) or FBP, the KM for PEP decreased 10-fold to 0.13±0.04 mM or 0.1±0.02 mM for the two activators, respectively, with lesser effects on Vmax (values of 245 pmols/min with or without FBP and 255 pmols/min with NCGC00031955: CID_654376, SID_851783). In contrast, variation of the concentration of ADP in the presence and absence of activators shows that the steady-state kinetics are not significantly affected (KM for ADP = 0.1mM in either condition). Thus, NCGC00031955 (CID_654376, SID_851783) and NCGC00030335 (CID_650361, SID_847943) activate hPykM2by increasing the enzyme’s affinity for PEP and have little effect on ADP kinetics. This is similar to what we observed for FBP, which agrees with previous reports demonstrating increased affinity for PEP as the reason for activation of hPykM2 by FBP.
References
- qHTS Assay for Activators of Human Muscle isoform 2 Pyruvate Kinase: Summary
- Boxer MB, Jiang JK, Vander Heiden MG, et al. Identification of activators for the M2 isoform of human pyruvate kinase Version 3. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); September 1, 2009.
- Walsh MJ, Brimacombe KR, Veith H, et al. 2-Oxo-N-aryl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-6-sulfonamides as activators of the tumor cell specific M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21(21):6322-6327. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.08.114
- Jiang, J.-K.; Boxer, M. B.; Vander Heiden, M. G.; Shen, M.; Skoumbourdis, A. P.; Southall, N.; Veith, H.; Leister, W.; Austin, C. P.; Park, H. W.; Inglese, J.; Cantley, L. C.; Auld, D. S.; Thomas, C. J. Evaluation of thieno[3,2-b]pyrrole[3,2-d]pyridazinones as activators of the tumor cell specific M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3387-3393


