ML200 : SMN2 (Survival Motor Neuron 2) Modulator
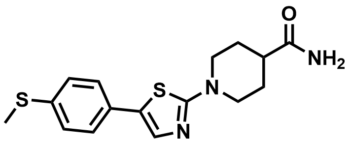
ML200
Target Name
Survival Motor Neuron 2
Target Alias
SMN2
Target Class
RNA Splicing Factor
Mechanism of Action
Modulator of SMN2
Biological / Disease Relevance
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), Splicing Modulator, Gene splicing, SMN2 splicing
In vitro activity
SMN expression (EC50)In vitro activity
SMN western blot (protein in patient fibroblast) (EC50)Target Information
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive disorder affecting the selective degeneration of survival motor neuron (SMN) in the spinal cord due to the deletion or mutations of the survival motor neuron gene 1 (SMN1). However, the human genome includes a second nearly identical gene called SMN2 which functionally differs from SMN1 by a critical nucleotide C to T transition residing in exon 7. Although SMN2 is able to produce a small portion of full length SMN protein, the majority of SMN2 RNAs undergo alternative splicing and produce truncated, proteolytically unstable SMN variants that are not able to replace the function of full length SMN protein. Therefore, increasing overall SMN production through up-regulation of SMN2 expression or through the variation of splicing rate has been postulated to be one of the potential therapeutic strategies for SMA. In this report, we detail the discovery of ML200 (CID 46907676; SID 99367992) as a novel arylpiperidine-based small molecule modulator of SMN protein production. ML200 had an AC50 of 31nM and gave 576% increase in fold induction of SMN promoter in the reporter assay. ML200 was confirmed by western blot analysis and gem count assay using SMA patient fibroblasts at low nanomolar range (37 nM). The structure property relationships (SPR) including microsomal stability, cell permeability and full time oral dosing in vivo pharmacokinetic studies were also investigated to address ADME properties. We anticipate that ML200 may serve as a useful lead for exploring the therapeutic benefits of SMN protein induction in SMA animal models, and ultimately in human clinical trials.
Properties

ML200
NCGC00187898
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 333.10 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N3OS2 | |||
| cLogP | 2.1745 | |||
| PSA | 59.22 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | 10mM in DMSO; 2.1 uM in PBS pH7.4 | |||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
CSC1=CC=C(C2=CN=C(N3CCC(C(N)=O)CC3)S2)C=C1
InChI:
1S/C16H19N3OS2/c1-21-13-4-2-11(3-5-13)14-10-18-16(22-14)19-8-6-12(7-9-19)15(17)20/h2-5,10,12H,6-9H2,1H3,(H2,17,20)
InChIKey:
ZFIWZVVHNRUILB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
In this report, we detail the discovery of a series of arylpiperidines as novel modulators of SMN protein production from a qHTS campaign of the 210,386 compound NIH Molecular Libraries of Small Molecule Repository. Systematic hit-to-lead medicinal chemistry efforts on this series dramatically improved both potency (up to 100 fold) and efficacy (up to 2 fold) of the series. Several lead compounds were identified as having very high potency, and a capacity to increase 3 to 7 fold induction of SMN promoter in the reporter assay including analogs 8l (AC50 = 77 nM, rate of induction = 710%), 8m (CID 46907676/ML200, current updated probe compound, AC50 = 31 nM, rate of induction = 576%), and 9a (AC50 = 12 nM, rate of induction = 326%). Furthermore, the activity of probe ML200 was confirmed by western blot analysis and gem count assay using SMA patient fibroblasts at low nanomolar range (37 nM). The structure property relationships (SPR) including microsomal stability, cell permeability and full time oral dosing in vivo pharmacokinetic studies were also investigated to address ADME properties. We anticipate that the updated probe compound ML200 may serve as a useful lead for exploring the therapeutic benefits of SMN protein induction in SMA animal models, and ultimately in human clinical trials.
Cellular activity - SMN protein expression (Western blot)
Summary /
ML200 and selected analogs (with potency below 150 nM in the reporter assay) were examined to evaluate the effect on the human SMN protein expression using fibroblasts from SMA patients. A fibroblast cell line from a type I SMA patient (3813 cell line) was incubated with different doses of the probe or its analogs and assessed the SMN protein level by quantitative western blotting (Figure 1). Resutls showed that the probe (8m) at concentration of 37 nanomolar increased the SMN protein level by 2-3 fold. The SMN protein level was decreased with the increasing of the drug concentration. This result matched with of bell-shaped curve observed in the luciferase reporter assay. Analog 9a (CID 46907666, NCGC00187872) showed a dose-dependent trend between 37 nM to 1 uM concentration and a decrease of protein level at 3 uM. Other selected agents 9c (CID 46907686, NCGC00187875), 8c (CID 46907733, NCGC00187892) and 8l (CID 46907708, NCGC00187894) all showed an up-regulation of SMN protein at concentrations ranging between 37 nM and 333 nM.
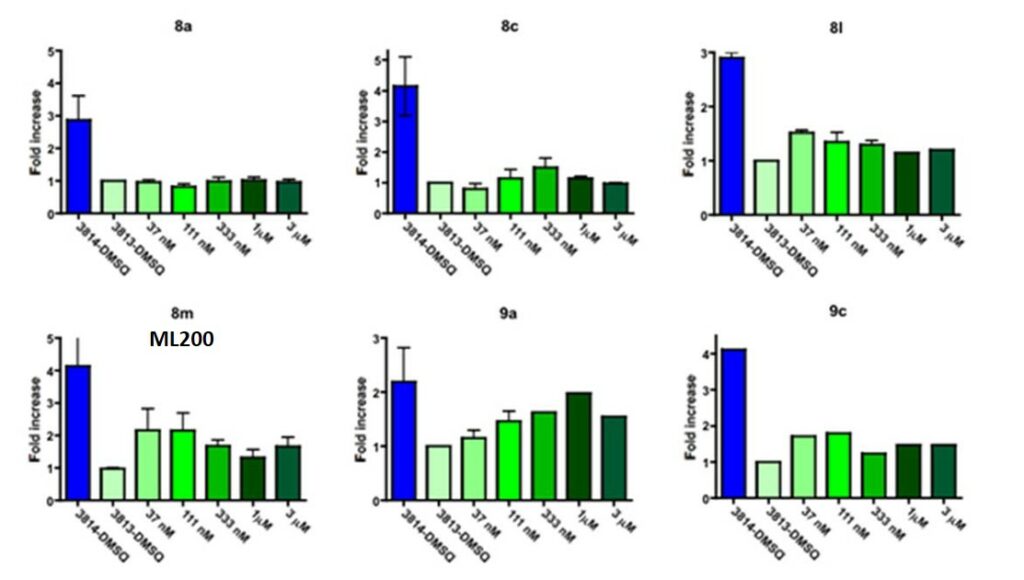
Figure 1. Quantification of western blot of SMN levels after treatment with drug compounds as indicated with different doses.
Cellular activity - Functional assay: SMN nucles foci formation assay
Summary /
Increase in SMN protein production led us to explore whether ML200 and its analogs had effect of on the overall number of SMN positive foci or gems in the nucleus. This would corroborate that the increased protein amounts represent indeed functional SMN protein. SMN protein is predominately a cytoplasmic protein in the nucleous SMN that localized in distinct punctuate bodies often referred to as gems (gemini of coiled Cajal bodies). There is a direct correlation between the number of gems and total SMN protein production in the cell. Gem counts are commonly used as another metric to score the amount total SMN protein expressed on a cell to cell basis. The number of nuclei with gems and the number of gems per cell were both significantly reduced in type I SMA cells (Coovert, 1997). Only 3.3% of nuclei have gems in fibroblast cells from SMA type I patients (cell line 3813), while 24.8% of nuclei have gems in fibroblast from a carrier parent (3814 cell line). We treated human type I SMA fibroblasts with increasing doses (37 nM – 3000 nM) of arylpiperidine analogs 8a, ML200 (8m), and 9a for 3 days and the number of gems per 100 nuclei were examined (Figure 2). The probe compound treatment yielded more than 2 fold of increase of the number of the gems at low 37 nM doses. With the concentration increased, the numbers of gems was reduced which agreed with the previous findings. Analog 9a also showed an 80% increase of the gem numbers at 37 nM to 1000 nM concentrations and slightly decreased at 3000 nM. However, analog 8a didn’t show any activity in this assay.
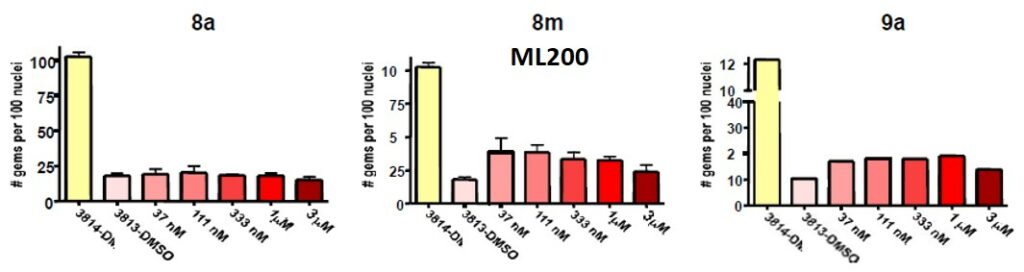
Figure 2. Number of gems per 100 nuclei after treatment with drug compounds as indicated with different doses.
In vitro activity - Mechanism of Action
Summary /
As initial studies to have a better understanding of the mode of action, we decided to use RT-PCR to measure RNA expression levels and exon 7 inclusion within our reporter cell line. Some analogs showed a small increase in total SMN-luciferase transcripts but there was almost no increase in exon 7 mRNA. Although the mechanism of SMN protein induction by this class of arylpiperidine analogs was still unclear, this result indicated that SMN activity for this series might be post-transcriptional, potentially stabilizing SMN protein and somehow reducing its degradation.
References
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen for Enhancers of SMN2 Splice Variant Expression: Summary
- Xiao J, Marugan JJ, Zheng W, et al. Discovery, SAR and Biological Evaluation of Aryl-thiazol-piperidines as SMN Modulators. 2010 Mar 19 [Updated 2011 May 5]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK63597/
- Coovert DD, Le TT, McAndrew PE, et al. The survival motor neuron protein in spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6(8):1205-1214. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.8.1205


