ML219 : LD (Lipid Droplet Formation) Modulator
ML219
Target Name
Lipid Droplet Formation
Target Alias
LD
Target Class
Lipid Storage Organelle
Mechanism of Action
Modulator of LD
Biological / Disease Relevance
Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Lipid Biogenesis
Cellular activity
LD assay (IC50)Target Information
Lipid droplets (LDs) are the universal lipid storage organelles. Lipids remobilized from LDs are used both for energy production and anabolic reactions, such as membrane biosynthesis. Nearly all mammalian components of adipocyte lipolysis are conserved in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, and the LDs of both species are coated with a similar set of proteins. These facts, combined with the rich genetic toolbox available for Drosophila melanogaster, positions the fruit fly as a prime in vivo model to study the mechanisms and pathways involved in lipid droplet biogenesis, regulation and breakdown.
The primary goal of the project was the identification of chemical probes decreasing the storage lipid content of cells. For this purpose, a cell-based assay using embryonic Drosophila melanogaster cells called “S3” was developed. Cells were incubated with the free fatty acid oleate to induce storage lipid deposition. Lipids are stored in specialized organelles, the so-called lipid droplets, which were stained with the lipophilic dye BODIPY493/503 (Invitrogen/Molecular Probes). We identified three unique chemotypes showing potent lipid droplet reduction phenotypes in the S3 cell based assay. The three probes identified, ML206, ML219 and ML220, had EC s of 8, 2 and 705 nM, respectively. While ML206 showed little translation into mammalian cell lines, both ML219 and ML220 showed moderate translation into acute myeloid leukemia (AML)12 cells.
Properties

ML219
NCGC00241426
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 462.6 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C27H30N2O3S | |||
| cLogP | 5.83 | |||
| PSA | 80.7 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | ||||
SMILES:
CCOC1=C(OCC)C=C(CCNC(C2=CC3=C(N2CC4=CC(C)=CC=C4)C=CS3)=O)C=C1
InChI:
1S/C27H30N2O3S/c1-4-31-24-10-9-20(16-25(24)32-5-2)11-13-28-27(30)23-17-26-22(12-14-33-26)29(23)18-21-8-6-7-19(3)15-21/h6-10,12,14-17H,4-5,11,13,18H2,1-3H3,(H,28,30)
InChIKey:
LGJRYJGSSSDVJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
In this Drosophila melanogaster cell-based screen, the probes ML206 (SID 99381576; CID 42288156), ML219 (SID 99460848; CID 46947845) and ML220 (SID 99460839; CID 46947860) show a potent LD reduction phenotype, with EC50s of 8 nM, 2 nM, and 705 nM, respectively. When looking at translation of this phenotype into mammalian cell lines, ML206 showed no significant activity in HepG2-, HeLa- or AML12-cells with <50% efficacy when compared to Triacsin C. Moderate translation into mammalian cells was seen for ML219, which gave an EC of 11 nM with 46% efficacy with AML12-cells. The third probe, ML220, also showed moderate translation in the AML12 cell line, reducing LD’s with an EC of 1.25 μM with >57% efficacy. With all three compounds showing extremely potent LD phenotypes in S3-cell based assays and modest translation into AML12-cells for ML219 and ML220, the utility of these compounds lies predominantly in Drosophila melanogaster studies, but they do show promise for use in mammalian systems. The target and mechanism of action for these probes in Drosophila melanogaster cells are not currently known, so studies using affinity chromatography, photoaffinity labeling and RNAi screening will hopefully elucidate their targets and provide insight into underlying mechanisms of LD biogenesis, maintenance and/or breakdown in mammalian systems.
Cellular activity - Selectivity and Cytotoxicity Assay
| Bioassay | ML219 (IC50) |
|---|---|
|
Cellular phenotype for lipid droplet storage |
2 nM |
|
Cytotoxicity (Anti-Target) |
11200 nM |
Summary /
Primary and all follow-up assays were performed in Drosophila melanogaster cells (S3), HeLa, HepG2 and AML12 cells, with activity seen in varying levels in 3 of these cell lines (S3, HepG2 and AML12) (Figure 1). Therefore, the compounds are deemed to have sufficient cell permeability/activity. The enantiomerically pure compounds have also been transferred to the assay provider’s lab, and Dr. Beller has confirmed activity in S3 cells using the same lipid-specific BODIPY dye, but with wide-field microscope-based analysis (Figure 2). These results support high and low potency for the (R) and (S) enantiomers respectively, as well as low cytotoxicity in S3 cells. No significant cytotoxicity (as compared to EC values) was seen for these probes (and the majority of their analogs) in any of the 4 cell lines. ML206, ML219 and ML220 showed >1000-fold cytotoxicity windows in S3-cells, with only minimal cytotoxicity at 46 μM.
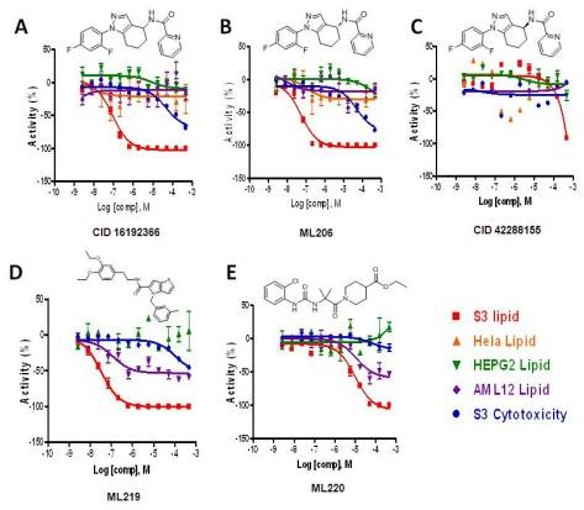
Figure 1. Confirmatory data for the probe compounds in S3, Hela, HepG2 and AML12 cells, along with cytotoxicity determined in S3 cells. The lipid reduction % Activity plotted is from the lipid data. A) The racemic compound CID16192366. B) The enantiomerically pure compound where the absolute configuration was confirmed as (R) for ML206. C) The enantiomerically pure compound where the absolute configuration was confirmed as (S) for CID42288155. D) The probe compound ML219 which also showed weak activity in AML12 cells. E) The probe compound ML220 which also showed weak activity in AML12 cells.
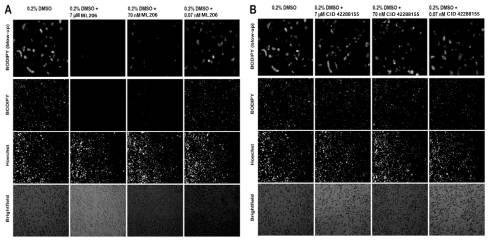
Figure 2. BODIPY and Hoechst staining of S3 cells treated with compounds. Data was collected at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Molecular Developmental Biology.
References
- PubChem link: qHTS Assay for Lipid Storage Modulators: Summary
- Boxer MB, Shen M, Zhang Y, et al. Modulators of Lipid Storage. 2010 Dec 15 [Updated 2013 May 3]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK153217/


