ML223 : RUNX1 (RUNX1 - CBFbeta interaction) Inhibitor
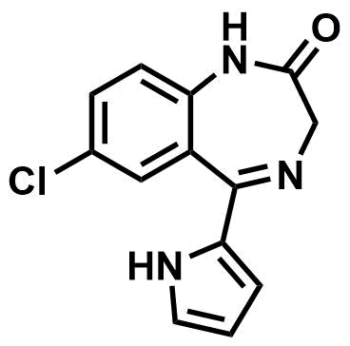
ML223
Target Name
RUNX1 - CBFbeta interaction
Target Alias
RUNX1
Target Class
Transcription Factor
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of RUNX1
Biological / Disease Relevance
Runx1; Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Subtype M4Eo; Leukemia; Cancer;
In vitro activity
RUNX1::CBFb (IC50)In vivo activity
Hematopoiesis in Zebrafish (IC50)Target Information
Disruption of protein-protein interactions is a promising therapeutic alternative in the field of oncology. Here, we disclose the discovery of a series able to disrupt the interaction of the transcription factor RunX1 with its activator core binding factor beta (CBFβ). This interaction is at the core mechanism of driving Acute Myeloid Leukemia Subtype M4Eo. The molecules described in this report, exemplified by ML223 (SID 109967253, CID 64983), show activity in relevant cell, zebra fish and mouse models, and are currently being considered for further drug development.
Properties

ML223
Ro5-3335
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 259.05 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C13H10ClN3O | |||
| cLogP | 1.7 | |||
| PSA | 57.2 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 30195-30-3 | |||
SMILES:
ClC1=CC=C2C(C(C3=CC=CN3)=NCC(N2)=O)=C1
InChI:
InChI=1S/C13H10ClN3O/c14-8-3-4-10-9(6-8)13(11-2-1-5-15-11)16-7-12(18)17-10/h1-6,15H,7H2,(H,17,18)
InChIKey:
XWNMORIHKRROGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML223 (SID 109967253, CID 64983) is observed to disrupt in vitro core binding factor beta’s (CBFbeta) interaction with the transcription factor RUNX1, whose aberrant activation is responsible for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subtype M4Eo. ML223 also interferes with the cellular proliferation of RUNX1-dependent cell lines, diminishes definitive hematopoiesis in zebrafish embryos, and provides efficacy in vivo with a CBFβ-MYH11 knock-in mouse model of leukemia. We are in the process of evaluating this series as a potential treatment for AML subtype M4Eo.
In vitro activity - Biochemical and Cellular Assay
Summary /
AlphaScreen primary screening assay of RUNX1::CBFbeta showed inhibition of the protein – protein interaction by ML223 in a dose response manner (Figure 1). Moreover, ML223 preferentially killed leukemia cells with CBF fusion genes (Figure 2); showing 6 – 5o fold more potent than those for leukemia cell lines without CBF fusion genes. This observation indicates that leukemia cells with CBF fusion gene are more sensitive to inhibitors of RUNX1-CBFbeta interaction than those without such fusion genes. In addition, ML223 showed selective killing of the CBFbeta-MYH11 containing ME-1 cells over normal CD34 cells (Figure 2).
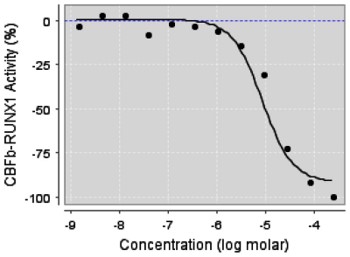
Figure 1. ML223 dose response curve of the inhibition of CBFβ-RUNX1 interaction in the primary screening assay.
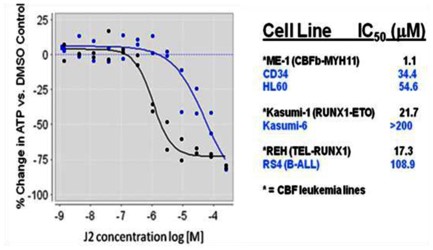
Figure 2. Selective cytotoxicity of ML223 for CBF leukemia cell lines. The graph shows % change of ATP contents in ME-1 (black line) and HL-60 (blue line) cells after treatment with ML223 at the indicated concentrations. ME-1 contains the CBFB-MYH11 fusion gene and HL-60 does not. The table on the right shows IC50 values for the listed cell lines. The ATP contents were measured by a luciferase based cell viability assay with −100% as 100% cell killing.
In vitro activity - ADME Assay
Summary /
We analyzed the probe compound ML223 and CID 284708 in microsomal stability and Caco-2 permeability assays. Table 1 shows microsomal stability of these compounds. The opened-ring analog CID 284708 has a relatively high intrinsic clearance, with 20% of parent compound left after 1 hour of incubation. The major metabolic process for CID 284708 is most likely generated through cytochrome P450-dependent oxidation. The probe ML223 has a spuriously high parent remaining; however, this experiment was simply used to gauge whether it would be appropriate to test compounds in vivo, and these results indicated that ML223 was not unstable. Table 2 presents permeability data on these compounds. Caco-2 data in Table 2 indicates that the probe compound, ML223, displayed much better cell permeability from apical to basolateral (A-B) than basolateral to apical (B-A), (efflux ratio = 0.7, [B-A/A-B]). The opened-ring analog CID 284708 owns poor cell permeability in both directions with high efflux ratio (1.5). These results demonstrate that the probe compound, ML 223, possesses sufficient in vitro ADME stability and permeability to warrant further testing in vivo. In fact, in a knock-in mouse model of leukemia, ML223 demonstrated activity by reducing the number of leukemic cells in blood and overall survival. Importantly, its activity synergized with the current standard of care treatment to improve survival even further (Figure 3).
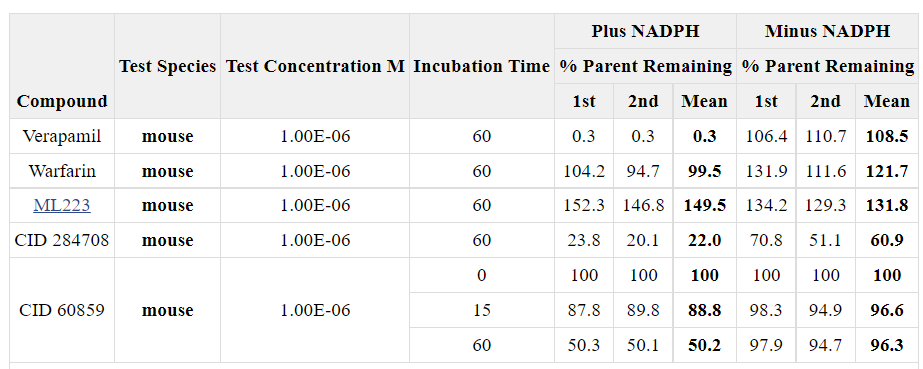
Table 1. Mouse microsomal stability assays after incubation for 60 minutes.
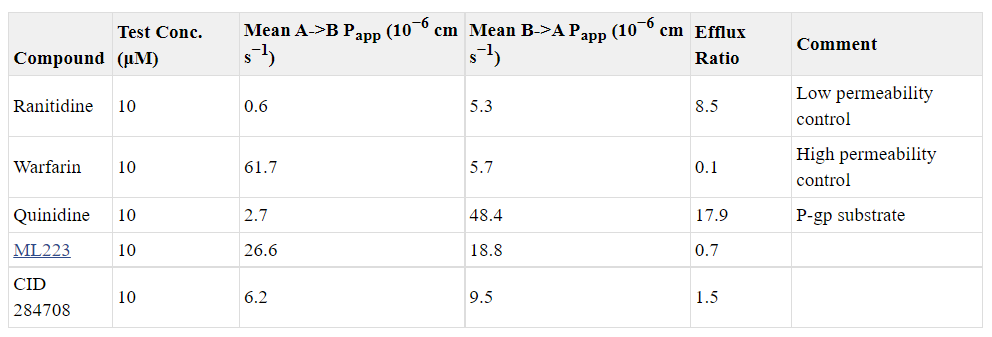
Table 2. Caco-2 permeability assays
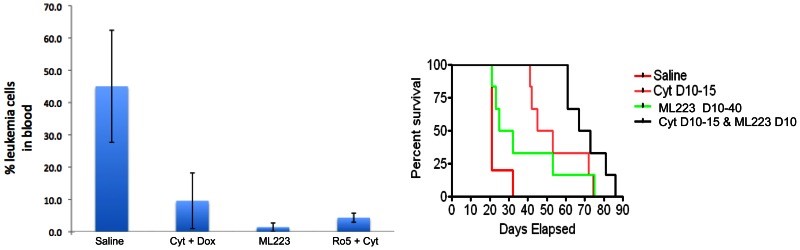
Figure 3. Activity of ML223 in a CBFB-MYH11 knock-in mouse model of leukemia. (Left) Reduced leukemia cell burden in mice treated with probe compound ML223. Cyt: cytarabine. Dox: doxorubicin. The data were collected 10 days after treatments started. N = 6 for each group except for saline, which had 5 mice. Leukemia cell percentages were represented by c-kit positive cells. (Right) Survival of leukemic mice treated with probe compound ML223 and standard of care compound cytarabine (Cyt). Control mice were given saline and Cyt mice were given cytarabine on days 10–15 after injecting CBF leukemia cells. ML223 was given on days 10–40 at 300 mg/kg/p.o. The data showed potential synergy between cytarabine and ML223.
In vivo activity - Zebrafish Definitive Hematopoiesis
Summary /
ML223 was further characterized in a Definitive Hematopoiesis in Zebrafish. This assay assessed ML223 activity in an in vivo setting without acute cellular toxicity and confirm blocking of the RUNX1-CBFbeta interaction, which is required for definitive hematopoiesis during embryogenesis. Results showed that treatment with ML223 blocked the definitive hematopoiesis (Figure 4) confirming inhibition of the RUNX1-CBFbeta interaction.
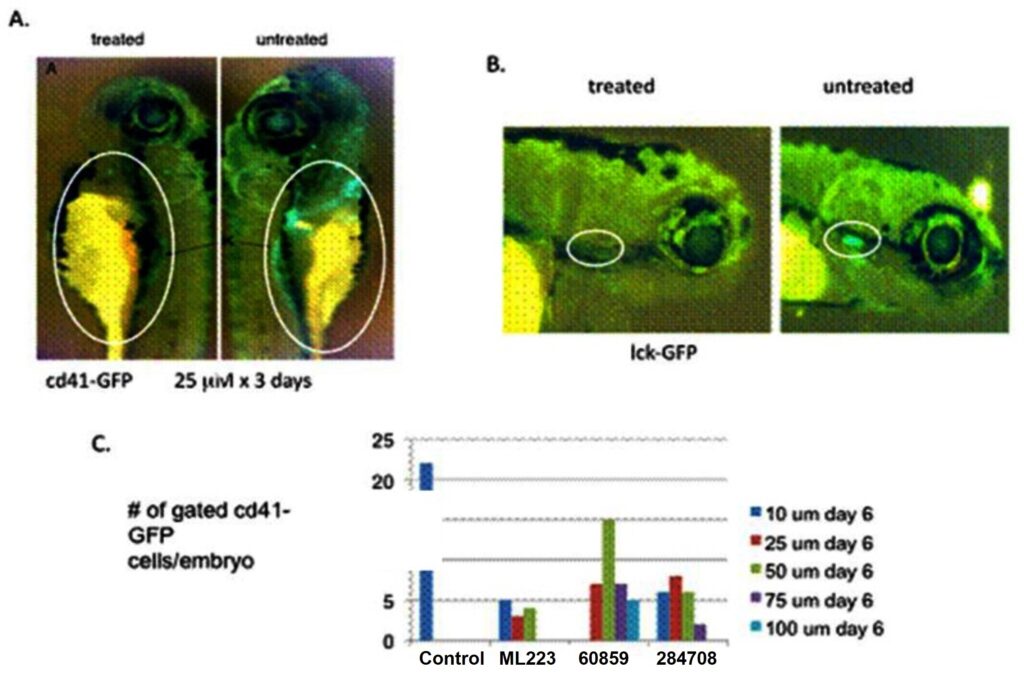
Figure 4. Three structurally related compounds (Figure 5) reduce definitive hematopoiesis in zebrafish embryos. A) cd41-GFP (platelet) transgenic embryos treated with ML223 at 25 μM for three days. B) lck-GFP (T cells) transgenic embryos treated with ML223 at 25 μM. C) Graph showing reduced numbers of cd41-GFP cells in embryos treated ML223, CID 60859 and CID 284708.
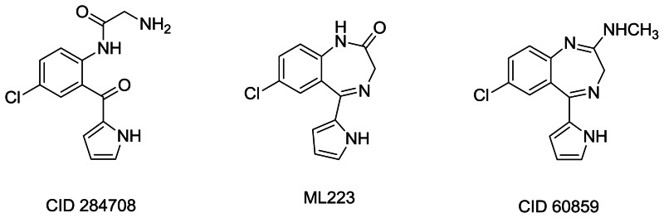
Figure 5. Chemical structures of the three compounds under study: the initial hit from primary screening CID 284708, ML223, and CID 60859.
References
- Quantitative High-Throughput Screen for Compounds Blocking the Interaction Between CBF-beta and RUNX1 for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Summary
- Marugan JJ, Xiao J, Zheng W, et al. ML223: A Small Molecule Probe With In Vivo Activity Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia Subtype M4Eo. 2011 Apr 4 [Updated 2013 Feb 28]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-.


