ML323 : USP1 (USP1/UAF1 Deubiquitinase Complex) Inhibitor
ML323
Target Name
USP1/UAF1 Deubiquitinase Complex
Target Alias
USP1
Target Class
Cysteine Protease
Mechanism of Action
Inhibitor of USP1
Biological / Disease Relevance
Ubiquitin–proteasome system; DNA damage response; deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB); Ubiquitination; translesion synthesis; Fanconi anemia pathways; USP1 biology
In vitro activity
USP1/ UAF1 (Ub-Rho)-In vitro activity
USP1/ UAF1 (Di-Ub)Target Information
Advances in pharmacological approaches to target the ubiquitin–proteasome system have revealed several potential new molecular targets within the ubiquitin machinery. Likewise, the functional consequences of ubiquitination and deubiquitination have recently been linked to a wide variety of critical biological processes well beyond just protein disposal. For example, the deubiquitining enzyme, ubiquitin-specific protease 1 (USP1), in association with its WD40 binding partner, UAF1 (USP1-associated factor 1), is a known regulator of DNA damage response and has been suggested as a promising target to improve the efficacy of the commonly used DNA damaging drugs by modulating the cancer cells’ ability to repair or tolerate DNA lesions. To further evaluate the therapeutic potential of targeting the USP1/UAF1 deubiquitinase complex, we conducted a quantitative high-throughput screen and a subsequent medicinal chemistry optimization campaign in pursuit of small molecules that inhibit USP1/UAF1. Herein, we describe the discovery and optimization of ML323 (SID 144116952 , CID 60167849) a probe molecule that displays reversible, nanomolar inhibitory activity and excellent selectivity toward USP1/UAF1. In addition, ML323 potentiates the cytotoxicity of cisplatin and increases endogenous monoubiquitination levels of both PCNA and FANCD2, two known cellular targets of USP1/UAF1. Lastly, ML323 possesses a promising in vitro ADME profile, suggesting its suitability for further testing in PK/PD studies.
Properties

ML323
NCGC00262306
| Physical & chemical properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 384.5 g/mol | |||
| Molecular Formula | C23H24N6 | |||
| cLogP | 4.6 | |||
| PSA | 68.5 Ų | |||
| Storage | ||||
| Solubility | ||||
| CAS Number | 1572414-83-5 | |||
SMILES:
CC(C1=C(C2=NC=C(C(NCC3=CC=C(N4C=CN=N4)C=C3)=N2)C)C=CC=C1)C
InChI:
InChI=1S/C23H24N6/c1-16(2)20-6-4-5-7-21(20)23-24-14-17(3)22(27-23)25-15-18-8-10-19(11-9-18)29-13-12-26-28-29/h4-14,16H,15H2,1-3H3,(H,24,25,27)
InChIKey:
VUIRVWPJNKZOSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity
Summary activity statement /
ML323 with its ability to potently and selectively inhibit USP1/UAF1 both in vitro and in a cellular context, enables biologists the evaluation of the USP1/UAF1 deubiquitinase complex as a target for therapeutic development. Ubiquitin-specific Protease 1 (USP1) is a deubiquitinating (DUB) enzyme implicated in DNA damage response through modulation of the ubiquitination levels of key proteins, PCNA and FANCD2, which play important roles in translesion synthesis and Fanconi anemia pathways, respectively [8]. Subsequent secondary and tertiary assay results also suggest that ML323 inhibitor may be used in combination with known DNA damaging agents, such as cisplatin, to potentiate the cytotoxicity [9]. In addition, ML323 addresses the limitations exhibited by the current probes. GW7647 and Pimozide, the first annotated USP1 inhibitors, display fairly promiscuous PubChem activity profile with a 9.9% and 12.0% hit rate respectively; while another compound C527 (Publication no. WO/2011/137320) also display limited selectivity across the deubiquitinase families (USP12/46, IC = 5.97 µM; USP5, IC = 1.65 µM; UCL-H3, IC = 2.18 µM). Therefore, given its favorable biochemical and physicochemical attributes, ML323 can be used by the research community to interrogate USP1 biology in vivo.
In vitro activity - Biochemical and Selectivity Assay
| Target Name | IC50/ EC50 | Fold Selectivity |
|---|---|---|
|
USP1/UAF1 (Ub-Rho) |
76 nM | |
|
USP1/UAF1 (Di-Ub) |
174 nM | |
|
USP2 |
> 114 mM | > 1500 |
|
USP7 |
> 114 mM | > 1500 |
|
USP8 |
> 114 mM | > 1500 |
|
USP46/UAF1 |
> 114 mM | > 1500 |
Summary /
ML323 inhibits USP1/UAF1 complex in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1) and exhibited greater than 1500 fold selectivity against USP1. Moreover, ML323 showed inhibitory effect only against the USP1/UAF1 (Figure 2).
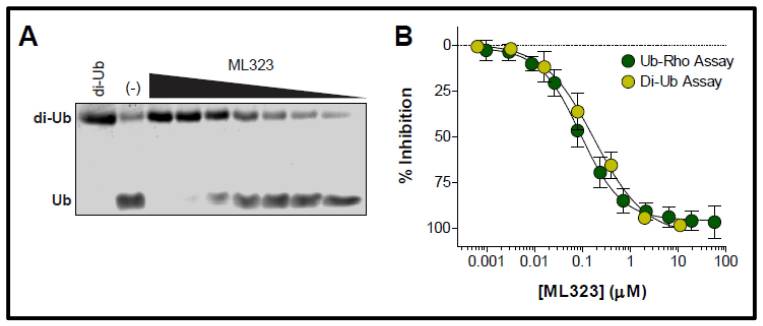
Figure 1. Dose response activity of ML323 (CID 60167849) in (A) SDS-PAGE gel analysis of K63-linked diubiquitin cleavage by USP1/UAF1 and (B) the Ub-rhodamine qHTS assay (green circles) and the K63-linked diubiquitin gel assay (yellow circles).
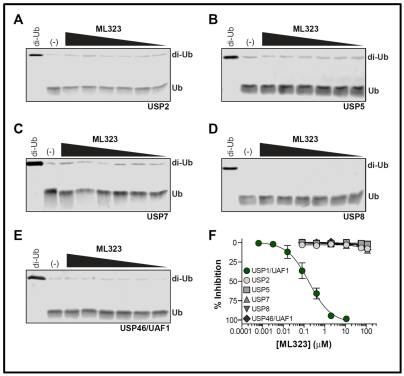
Figure 2. Evaluation of the probe ML323 in SDS-PAGE gel assays of the cleavage of K63-linked diubiquitin by (A) USP2, (B) USP5, (C) USP7, (D) USP8, and (E) USP46/UAF1 in the presence of ML323. Graphical representation (F) of the percent inhibition of the different USPs (A-E) by ML323 showed dose-response inhibition only against USP1/UAF1.
In vitro activity - Inhibition of Cellular Activity of USP1/UAF1
Summary /
Activity profile of the probe ML323 showed treatment of human cells (HEK293T and H596) cells by USP1/UAF1 inhibitors led to a dose dependent increase in PCNA and FANCD2 monoubiquitination (Figure 3).
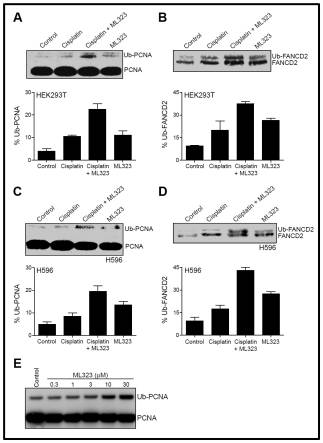
Figure 3. HEK293T (A and B) and H596 (C and D) cells were treated with 100 µM cisplatin (lane 2), 30 µM ML323 (lane 4), or in combination (lane 3). Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-PCNA antibody (A and C) or anti-FANCD2 antibody (B and D). The percentages of monoubiquitinated PCNA or FANCD2 were reported below each blot. E) Dose-dependent increase in Ub-PCNA in HCT116 cells treated with ML323.
In vivo activity - Cytoxicity and Clonogenicity Assay
Summary /
The Cytotoxicity of cisplatin and ML323 were tested as a single agent or in combination on cisplatin-resistant NSCLC (H596) cells. Results showed a synergistic effect of the probe ML323 with cisplatin against H596 cell line (Figure 4).
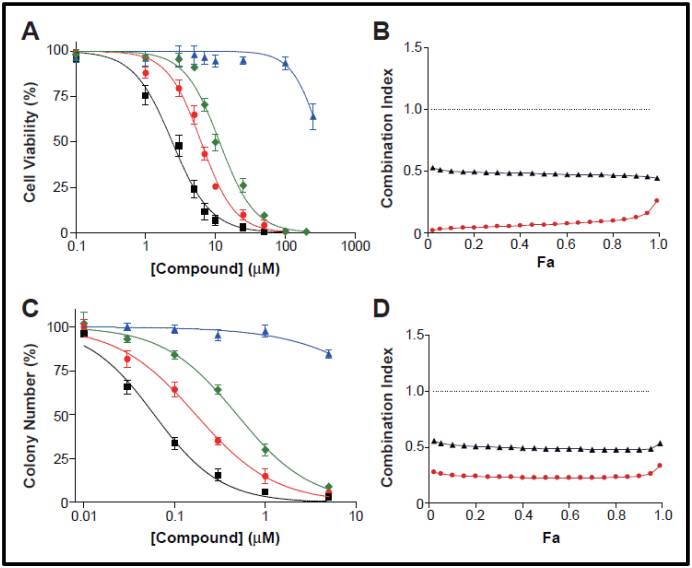
Figure 4. Cytoxicity and Clonogenicity Assay. A) Cytotoxicity of cisplatin alone (green diamond), ML323 (blue triangle), or a combination of cisplatin and ML323 at ratios of 1:1 (red circle), 1:4 (black square) in CCK assay and (C) colony formation assay. (B) Combination index analysis of the synergistic interaction of cisplatin and (D) ML323 in CCK assay and colony formation assay. Ratios of 1:1 and 1:4 were shown as black triangles and red circles, respectively. The dashed horizontal line represents a combination index = 1. Results indicated the synergistic effect of the probe ML323 with cisplatin.
In vitro activity - ADME Profile
| Compound | PBS buffer solubility at pH 7.4 (uM) | Log D at pH 7.4 | Rat Liver Microsome Stability (T 1/2) | Caco-2 (A->B) P app (10^-6 cm/s) | Caco-2 (B->A) P app (10^-6 cm/s) | Efflux Ratio | PBS buffer stability at pH 7.4 (48h) | Mouse Plasma Stability (2h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ML323 |
86 | 1.97 | 12 min | 22.98 | 20.78 | 0.90 | 99% | 99% |
Summary /
ML323 showed good kinetic solubility and bioavailability as indicated by a favorable results in solubility, Log D, and Caco-2 permeability. The probe compound also showed no degradation without NADPH present over a 1 hour period.
References
- Inhibitors of USP1/UAF1: Summary
- Dexheimer TS, Rosenthal AS, Liang Q, et al. Discovery of ML323 as a Novel Inhibitor of the USP1/UAF1 Deubiquitinase Complex. 2012 Oct 23 [Updated 2014 Sep 18]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK259186/


